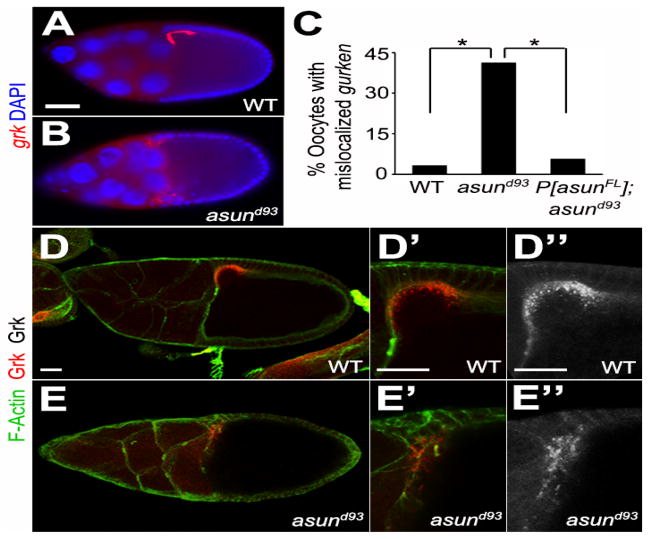
Figure 4. Localization of grk transcripts and Grk protein in asund93 oocytes.
(A–B) Fluorescent in situ hybridization of stage 9 egg chambers using grk probe (red). Dorsal, top; anterior, left. grk mRNA localization is tightly restricted to the anterior-dorsal region of the oocyte in wild-type egg chambers (A). In asund93 egg chambers, grk transcripts are more diffusely localized throughout the anterior oocyte (B). Scale bars, 50 μm. (C) Quantification of abnormal gurken mRNA localization in wild-type, asund93, and rescued asund93 egg chambers (>100 chambers scored per genotype) by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Asterisks, p<0.0001. (D–E″) Maximum projection confocal images of stage 10 wild-type and asund93 egg chambers stained with Gurken (red; grayscale in D″ and E″) and F-Actin (green; cell membrane marker). Anterior, left; dorsal, top. Gurken protein localizes normally to the anterior-dorsal region of asund93 oocytes (E, E′, E″), but occasionally with a lower intensity and more diffuse pattern than that observed in wild-type oocytes (D, D′, D″). Scale bars, 20 μm.