Figure 2.
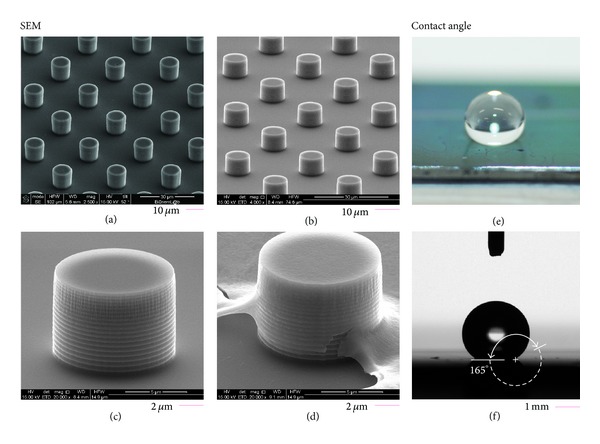
SEM images of the micropillars composing the superhydrophobic device; the pillars are arrayed to form regular geometries and these cover regions as large as several hundreds of microns without defects or imperfections ((a), (b)). Larger magnifications reveal, at smaller scales, the conductive PEDOT:PSS thin film ((c), (d)). A fluorocarbon polymer (C4F8) is finally deposited on the devices which, on account of their hierarchical structures bridging different length scales [30], exhibit an increased hydrophobicity with contact angles as large as 165° ((e), (f)).
