Figure 3.
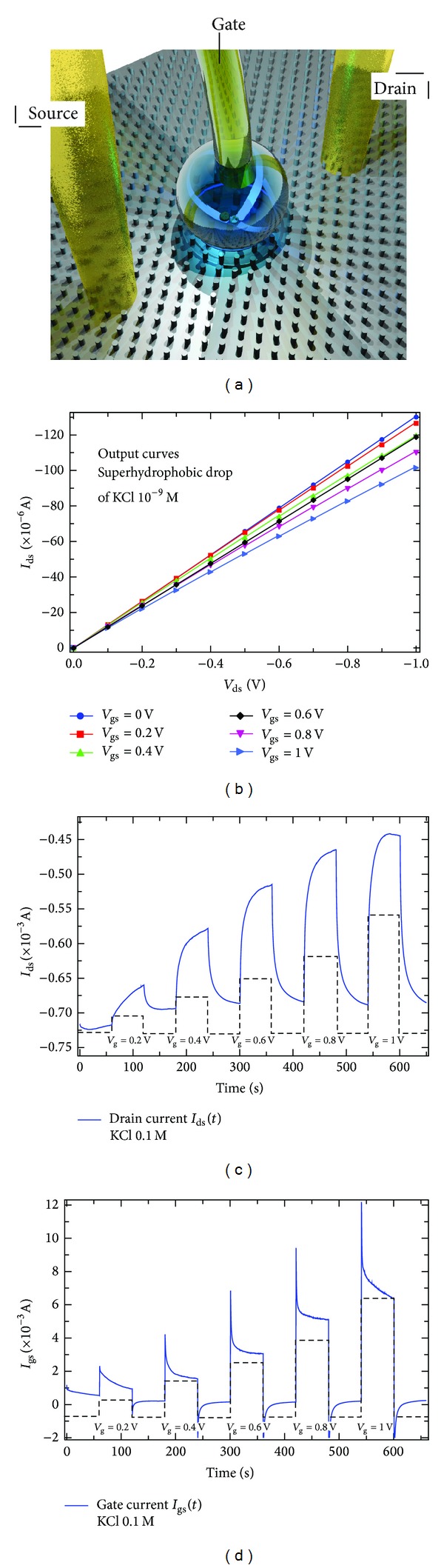
The devices have been tested using a solution of KCl in water to evaluate their electric characteristics and their sensing performances. In (a) the sketch of the device architecture is reported. Two electrodes, source and drain, are connected to the PEDOT:PSS on the substrate surface. Between the two metal electrodes a drop of electrolyte solution is suspended over the pillar surface with a gate silver electrode on the top. In (b), the transfer characteristic of the transistor at 10−9 M is reported. The transfer characteristic shows the working characteristics of the OECT on the superhydrophobic surface. In (c), the measurement of I ds current in function of time for increasing gate voltages for KCl at 0.1 M is reported. In (d), the current between gate and source in function of time during the same increasing gate voltages is instead reported.
