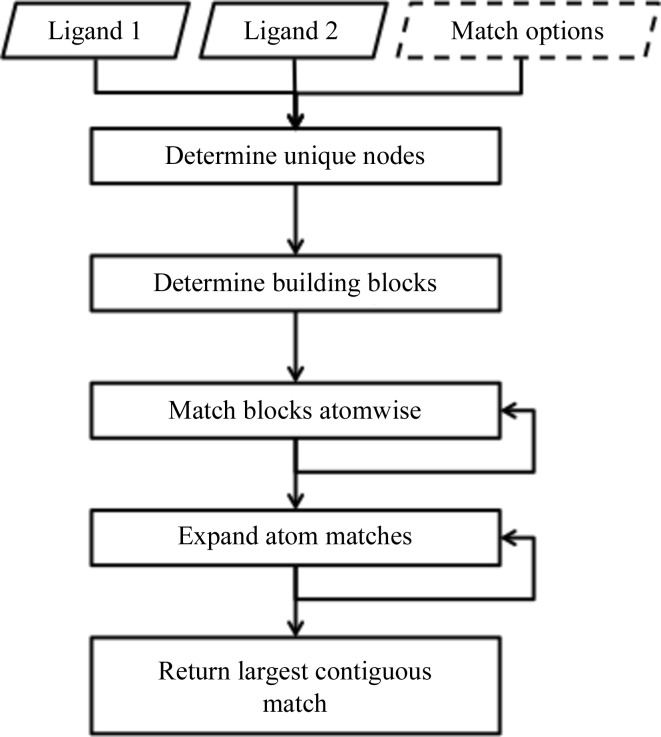
Figure 4.
Overview of the matching algorithm used in eLBOW to associate analogous atoms in two molecules. The input consists of the two ligands in any accepted format (e.g. SDF). Unlike routines such as phenix.superpose_ligands, in GLR the match options are fixed and not exposed to the user through PHIL instructions. Both the matching of building blocks and the expansion of atom matches are iterative. These steps are repeated to generate the greatest number of atomic matches.