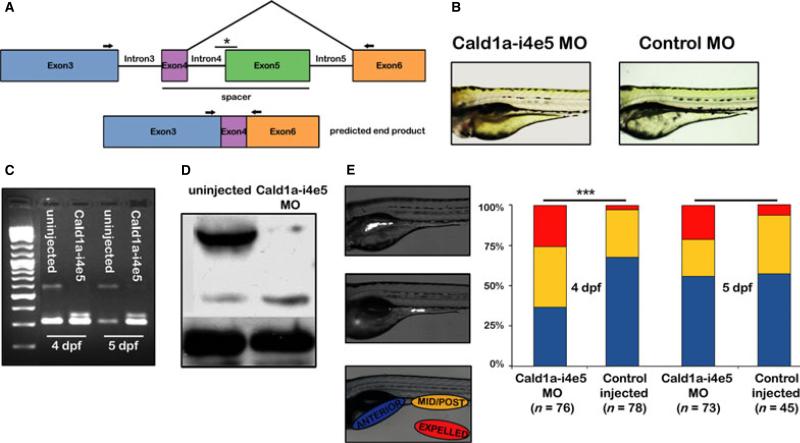
Figure 4.
h-CaD deficiency enhances intestinal peristalsis in zebrafish larvae. (A) Schematic depicting isoform specific targeting of the high molecular weight cald1a transcript by a splice blocking morpholino (Cald1a-i4e5 MO). The exon 5 splice acceptor is targeted (*). (B) Normal morphology of 4 dpf larvae injected with Cald1a-i4e5 MO and control morpholinos. (C) RT-PCR of intestinal cDNA from Cald1a-i4e5 MO larvae using exon 3 and exon 6 primers (arrows in panel 3A) shows markedly reduced expression of the high molecular weight cald1a transcript. (D) Western blot using intestinal protein from Cald1a-i4e5 MO larvae shows reduced levels of h-CaD with slightly increased l-CaD levels. Increased protein corresponding to l-CaD likely reflects additional protein translated from modified transcript only 12 amino acids larger than l-CaD. (E) Images of live 5 dpf larvae that ingested fluorescent microspheres located in anterior and mid-posterior intestine, respectively. Color scheme in bar graph depicts bead location indicated in lateral image of larva (lower panel). Cald1a-i4e5 MO larvae show increased propulsive peristalsis at 4dpf (chi-squared test, ***P < 001). 5dpf P-value = 0.08, likely due to transient effect of morpholino knockdown.