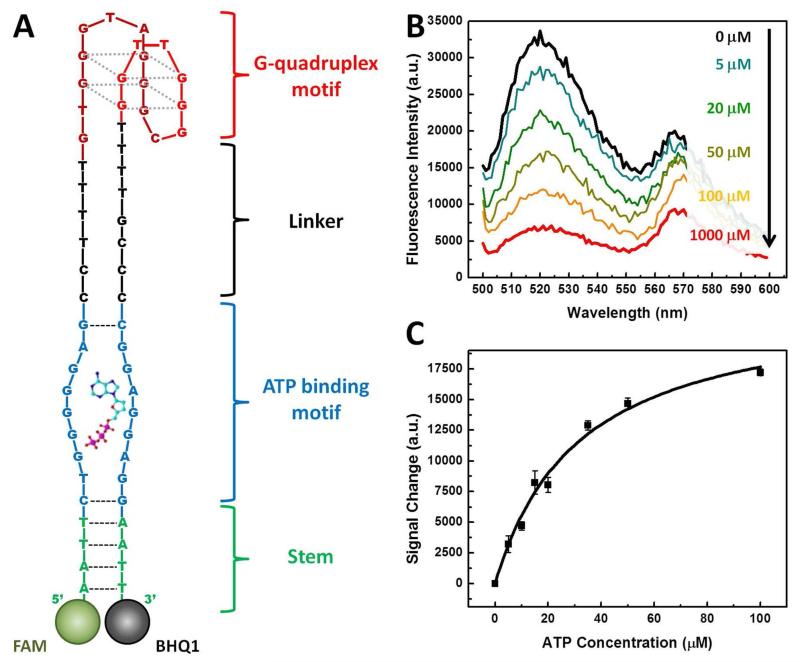
Figure 4.
Characterization of ATP-induced conformational change in SSA-1. (A) The expected structure of SSA-1 after the release of the cargo strand. The structure consists of four domains; the G-quadruplex motif (red) is connected through an unhybridized linker (black) to an ATP binding motif (blue), which is in turn adjacent to a short stem. To confirm that the structure undergoes a shape change upon ATP binding, we labeled the 5′ end with a fluorophore (FAM) and the 3′ end with a quencher (BHQ1). (B) SSA-1 emits strong fluorescence in the absence of ATP. As ATP concentration increases, the fluorescence signal decreases as the conformational change of SSA-1 brings the quencher into close proximity with the fluorophore. (C) Measurements of ATP concentration-dependent signal decrease yield an EC50 of 31.8 ± 4.8 μM at a 30 nM concentration of SSA-1/cargo strand (1:1.5 ratio).