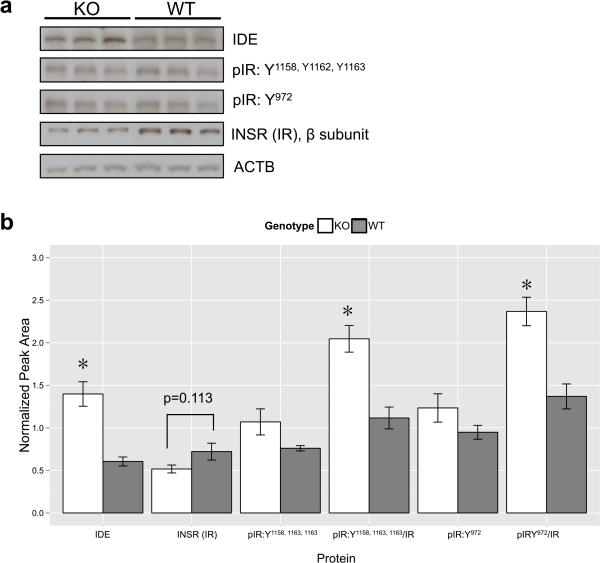
Figure 7. Alpha7 knockout mice display differential basal expression of insulin-related proteins in the nucleus acumbens.
a) Representative immunoblots of nucleus accumbens samples from individual mice. IDE=insulin-degrading enzyme, pIR=phosphorylated insulin receptor (Y= tyrosine residue phosphorylated), INSR/IR=β subunit of the insulin receptor, ACTB=β-actin). b) Quantitation and statistical analyses of immunoblot samples (nKO=6, nWT=5) revealed that IDE protein levels as well the degree of phosphorylation of the total insulin receptor were significantly increased in alpha7 KO mice compared to WT mice, while total insulin receptor levels showed a trend for being decreased compared to WT mice. All proteins were normalized to ACTB (* = p<0.01).