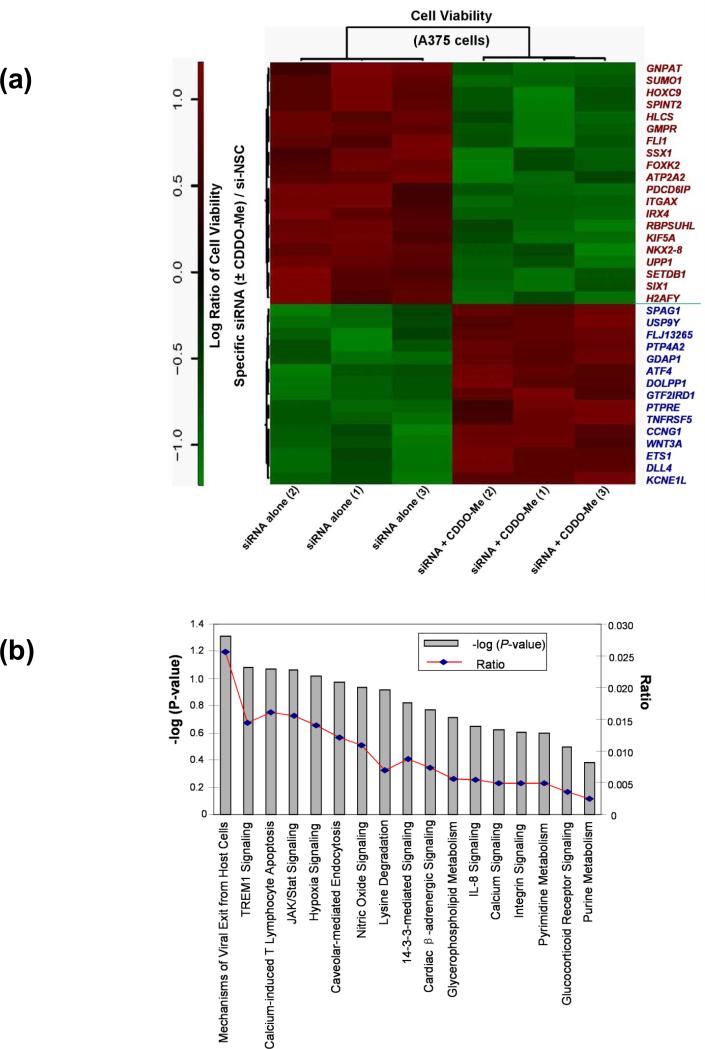
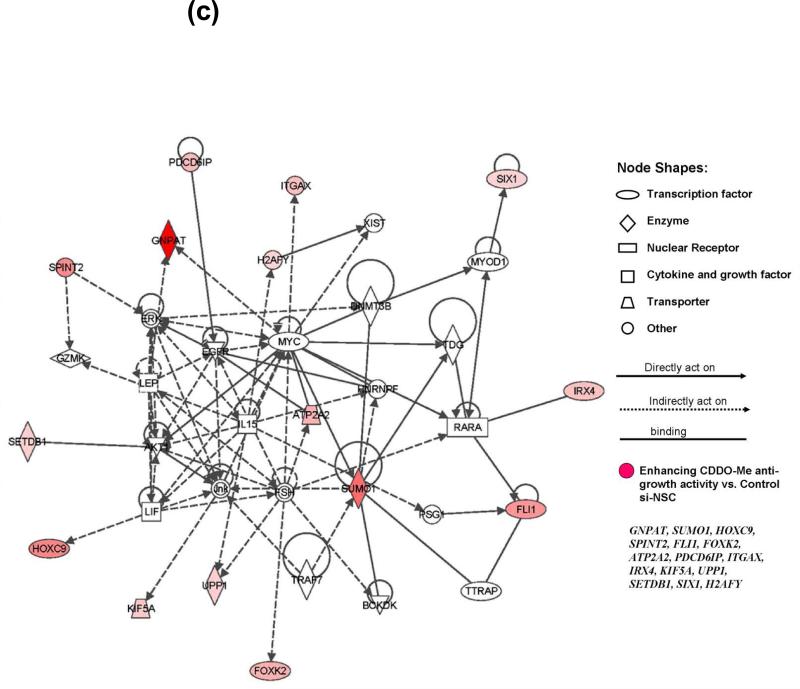
Figure 2. Identification of modulators for CDDO-Me response in melanoma cells by synthetic lethal siRNA screen.
(a) Heatmap of 35 specific siRNAs and related genes that can significantly modulate the response to CDDO-Me in A375 cells. The rotio (siRNA ± CDDO-Me/si-NSC control) of the cell viability of each gene (siRNA) is shown in three replicates. The downregulation of 20 genes on the top panel of heatmap (red text) could significantly potentate the anti-growth activity of CDDO-Me in A375 cells (P<0.001), whereas the downregulation of 15 genes on the bottom panel (blue text) could significant reverse the antigrowth activity of CDDO-Me (P<0.001). (b) The IPA studies determine that 35 genes identified by siRNA screen participate in 17 canonical signaling pathways. (c) Functional network analysis by IPA. The top scoring signaling network regulating cell development, growth, and proliferation composed of multiple genes, which include 15 genes identified from our synthetic lethal RNAi screening (red-colored). Nodes represent genes, with their shape representing the functional class of the gene product, and the edges indicate the biological relationship between the nodes.