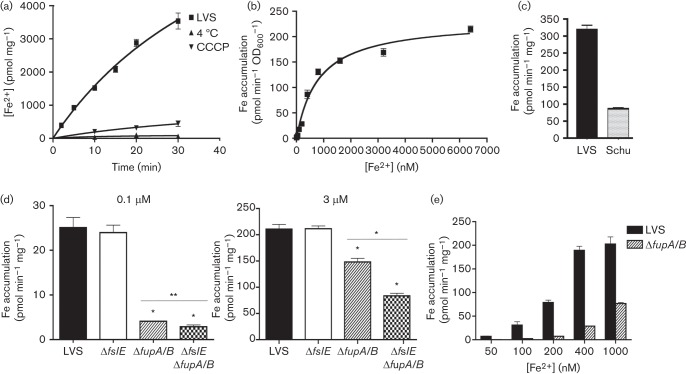
Fig. 1.
Ferrous iron uptake in LVS and mutants. (a) Kinetics of 55Fe2+ transport by LVS. LVS bacteria were grown in iron-limiting che-CDM for 16 h and then diluted and further grown under iron limitation for 22 h. The bacteria were washed and incubated with 7.4 µM 55Fe2+ at 37 °C and incorporation of 55Fe2+ over time was determined by scintillation counting. Transport reactions were carried out in parallel at 4 °C and with bacteria that had been pretreated with carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone. (b) Rate of 55Fe2+ transport by LVS plotted as a function of ferrous iron concentration in the uptake reaction. (c) Rate of 55Fe2+ transport by LVS and Schu S4 at 3 micromol ferrous iron. (d) Rates of high-affinity (0.1 µM) and low-affinity (3 µM) ferrous iron transport in LVS and the ΔfslE and ΔfupA/B mutants after growth in iron-limiting media for 20 h. (e) Comparison of ferrous iron transport rates of LVS and ΔfupA/B mutant over a range of iron concentrations. 55Fe accumulation was normalized to protein content or to cell density (OD600). Values are plotted as means with se. Significance was calculated relative to LVS values: *P<0.001, **P<0.02.