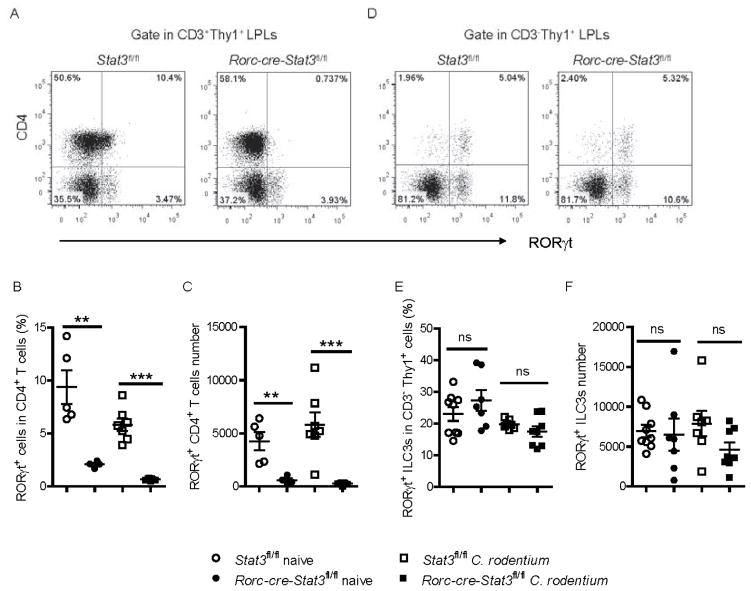
Figure 6. The development of RORγt+ T helper cells, but not RORγt+ ILCs is dependent on STAT3 signaling.
(A–F) Colonic LPLs were isolated from Stat3fl/fl and Rorc-cre-Stat3fl/fl littermate mice before or 5 days after C. rodentium infection.
(A, D) RORγt and CD4 expression were analyzed in colonic LPLs from naïve mice by flow cytometry after gating on Thy1+ CD3+ adaptive lymphocytes and Thy1+ CD3− innate lymphoid cells.
(B, C) Percentage of RORγt+ cells in the CD4+ CD3+ T cell population, as well as the absolute numbers of RORγt+ CD4+ T cells in the colons of naïve and C. rodentium infected Stat3fl/fl and Rorc-cre-Stat3fl/fl mice are shown.
(E, F) Percentage of RORγt+ cells in the CD3− Thy1+ ILCs population, as well as the absolute numbers of RORγt+ ILCs in the colons of naïve and C. rodentium infected Stat3fl/fl and Rorc-cre-Stat3fl/fl mice are shown.
**P<0.01, ***P<0.001; ns, no significant difference (Student’s t-test). Data are representative of three independent experiments (mean ± s.e.m.). Each dot represents one individual mouse (B, C, E, F). See also Figure S6.