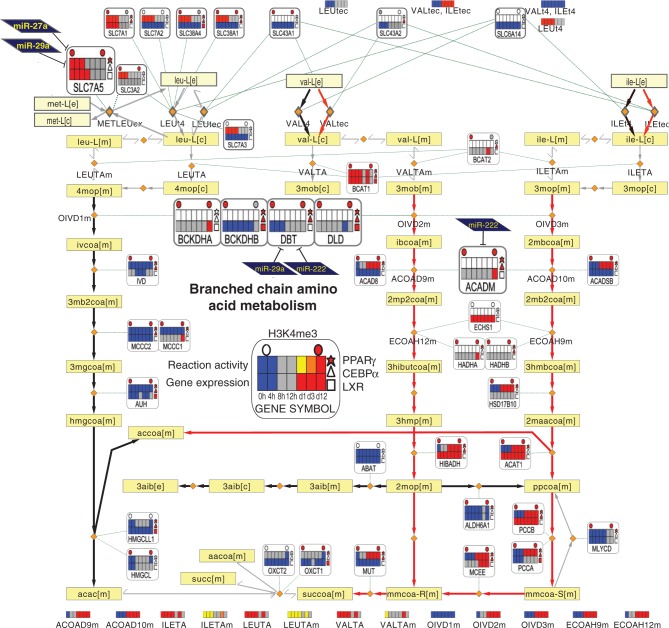
Figure 7.
Integrated metabolic pathway of BCAA metabolism. The BCAA (valine, leucine and isoleucine) metabolism pathway is shown. The metanode and edge representation is identical to Figure 6. While leucine degradation is predicted inactive in both preadipocytes and adipocytes (left part), the degradation of both valine and isoleucine is predicted to become active in adipocytes (red edges). The respective end products acetyl-CoA and succinyl-CoA can be fed into the TCA cycle. The important intermediates malonyl-CoA and acetoacetate link to lipogenesis or ketone body formation, respectively. This pathway has similarities with FAO, sharing the enzyme ACADM and the metabolite propionyl-CoA (ppcoa[m]). The metanodes indicate that two nodes are associated with both TFs and miRNAs: The component of the large multienzyme complex, DBT, is associated with PPARγ, CEBPα, miR-29a and miR-222, while among BCAA transporters contained in Recon1, SLC7A5 is associated to PPARγ, miR-27a and miR-29a. The genes discussed further in the text are shown as larger metanodes for clarity.