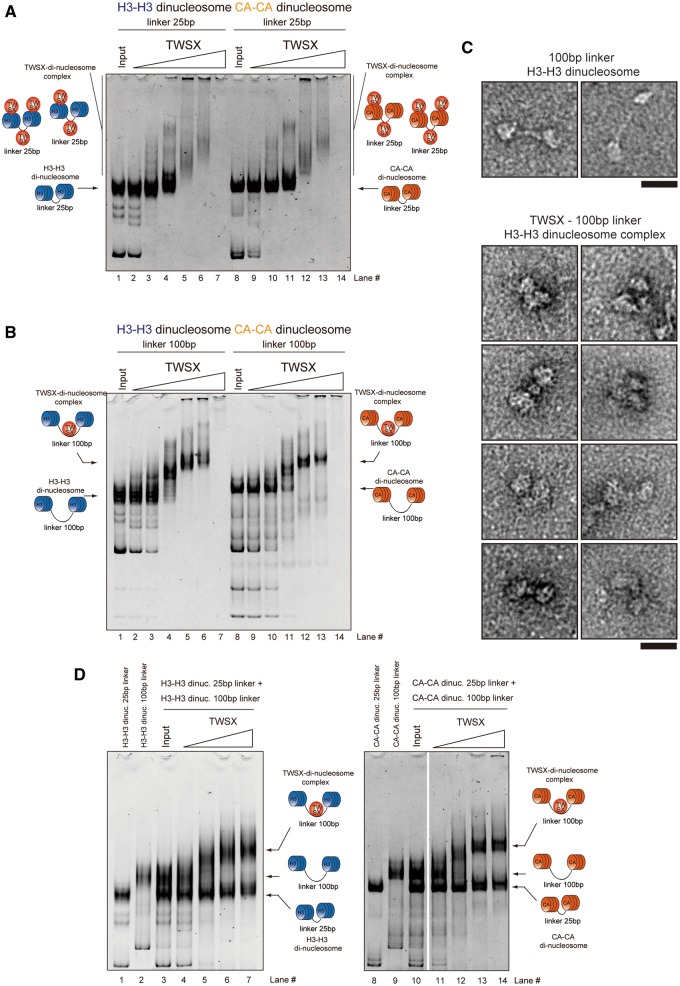
Figure 2.
The CENP–T–W–S–X complex preferentially binds to ∼100 bp linker DNA rather than nucleosomal DNA. (A) Binding assays for the CENP–T–W–S–X complex to di-nucleosomes (0.1 µM) containing either CENP–A or histone H3 with 25 bp linker DNA. Different concentrations of the CENP–T–W–S–X complex (lane 2, 9 - 0.1 µM; lane 3, 10 - 0.2 µM; lane 4, 11 - 0.4 µM; lane 5, 12 - 0.8 µM; lane 6, 13 - 1.0 µM; lane 7, 14 - 2.0 µM) were used for these assays. (B) Binding assays for the CENP–T–W–S–X complex to di-nucleosomes (0.1 µM) containing either CENP–A or histone H3 with 100 bp linker DNA. Different concentrations of the CENP–T–W–S–X complex (lane 2, 9 - 0.1 µM; lane 3, 10 - 0.2 µM; lane 4, 11 - 0.4 µM; lane 5, 12 - 0.8 µM; lane 6, 13 - 1.0 µM; lane 7, 14 - 2.0 µM) were used for these assays. (C) Visualization of the CENP–T–W–S–X-di-nucleosome complexes by an electron microscope (lower images). Images of di-nucleosomes in the absence of the CENP–T–W–S–X complex are also shown (upper images). Bar, 20 nm. (D) Competitive binding assays for the CENP–T–W–S–X complex to di-nucleosomes with 25 bp DNA and 100 bp DNA. Histone H3 nucleosomes were used in the left gel and CENP–A nucleosomes were used in the right gel. Different concentrations of the CENP–T–W–S–X complex (lane 4, 11 - 0.2 µM; lane 5, 12 - 0.4 µM; lane 6, 13 - 0.8 µM; lane 7, 14 - 1.0 µM) were used for these assays.