Figure 6.
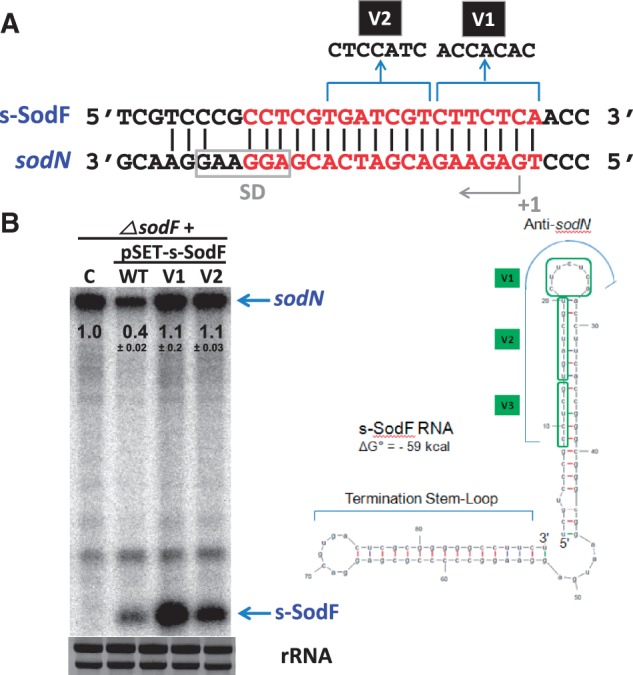
Sequence-specificity of s-SodF RNA to inhibit sodN expression. (A) Variants of s-SodF were created by changing sequences in the anti-sodN region. V1 harbor changes of seven nucleotides that correspond to the predicted loop region in anti-sodN sequence. V2 harbor changes in the subsequent seven nucleotides. (B) Effect of s-SodF mutations on the level of sodN mRNA. The mutated s-SodF genes were cloned in pSET152-based vector pSET162 with ermE* promoter, and incorporated into the chromosome of ΔsodF strain through phage attachment site, as done for the wild-type s-SodF construct used in Figure 5. The ΔsodF cells with parental vector control (C), wild type (WT) and variants (V1, V2) of s-SodF genes were grown in YEME to OD of 0.8. RNA samples were obtained from cells as in Figure 5, without rifampicin chase. A representative gel from three independent experiments was presented, and marked with the quantified values of the average ± SD for sodN mRNA.
