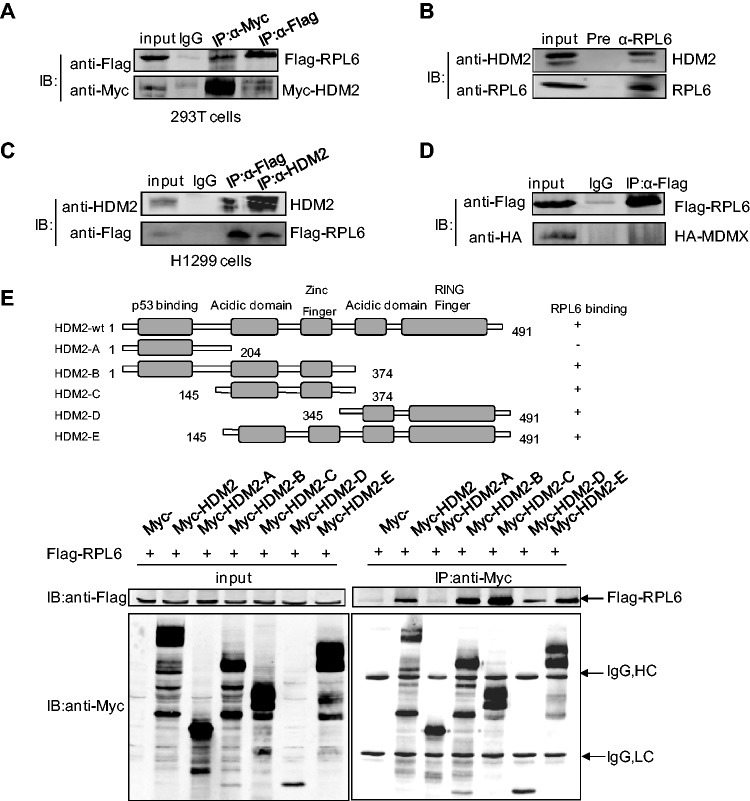
Figure 1.
RPL6 interacts with HDM2. (A) Interaction between exogenous RPL6 and HDM2. HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-RPL6 and Myc-HDM2. Thirty-six hours after transfection, cells were harvested and lysed with 1 ml NP-40 cell lysis buffer. The cell lysate was divided equally into the three IPs, and 3% input was loaded as the input and the remaining was immunoprecipitated with control IgG, anti-Flag or anti-Myc antibody followed by immunoblotting (IB) with indicated antibodies. (B) Interaction of endogenous HDM2 and RPL6 in HCT116 cells. The lysates of HCT116 were immunoprecipitated with anti-RPL6 or preimmune serum followed by IB with anti-HDM2 and anti-RPL6 antibodies. (C) RPL6 interacts with HDM2 in p53-null H1299 cells. Cell lysates were prepared from H1299 cells and Co-IP assay was performed with anti-Flag, anti-HDM2 or control IgG followed by IB with anti-HDM2 and anti-Flag antibodies. (D) Flag-RPL6 does not interact with HA-MDMX in HEK293T cells. Cells were transfected with Flag-RPL6 and HA-MDMX and harvested for Co-IP assay with the indicated antibodies. This experiment has been performed three times. (E) Mapping of the HDM2 domains for RPL6 binding. HCT116 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing full-length Flag-RPL6 and different truncation constructs of Myc-HDM2. Immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed with anti-Myc antibody followed by IB with anti-Flag antibody. A diagram for the truncations of HDM2 used in this assay was shown on top.