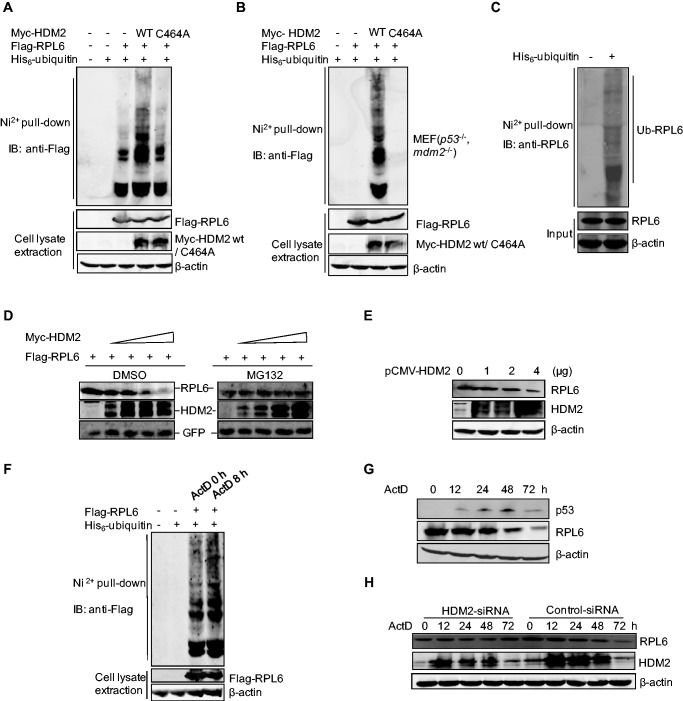
Figure 6.
RPL6 is a substrate of the HDM2 E3 ubiquitin ligase. (A and B) Ubiquitination of RPL6 increases in the presence of HDM2. HCT116 cells (A) and p53−/−, mdm2−/− MEFs (B) were transfected with plasmids as indicated for 20 h. Cells were incubated with 30 µM MG132 for 8 h before harvesting. Cell lysates were then subjected to in vivo ubiquitination assay. (C) Endogenous RPL6 is ubiquitinated. HCT116 cells were transfected with His-ubiquitin and in vivo ubiquitination assay was performed to detect the ubiquitination of endogenous RPL6 with anti-RPL6 antibody. (D) HDM2 decreases the abundance of ectopically expressed RPL6 in a dose-dependent manner. HCT116 cells were transfected with increasing amount of Myc-HDM2 (0, 1, 2, 3, 4 µg) and Flag-RPL6 (1 µg) as indicated. Twenty-four hours later, cells were treated with MG132 (30 μM) for 9 h. (E) HDM2 decreases the level of endogenous RPL6. A549 cells were transfected with increasing amount of pCMV-HDM2. Forty-two hours after transfection, cells were harvested and the level of RPL6 was detected with anti-RPL6 antibody. (F) The ubiquitination of RPL6 increases in response to ActD treatment. HCT116 cells were transfected with plasmids as indicated. 24 h after transfection, cells were incubated with ActD (5 nM) for indicated time before harvesting. Cell lysates were subjected to in vivo ubiquitination assay. (G) The abundance of p53 reduces following the decrease of RPL6 after prolonged ActD treatment. U2OS cells were treated with 5 nM ActD for indicated times. Cells were harvested and subjected to IB with anti-p53, anti-RPL6 and anti-β-actin antibodies. (H) Decrease of RPL6 in response to ActD treatment is HDM2-dependent. A549 cells were transfected with Small Interfering RNA (siRNA)-control or siRNA-HDM2 and cells were subjected to ActD treatment for indicated times. The levels of RPL6 and HDM2 were examined by IB with anti-RPL6 and anti-HDM2 antibodies, respectively.