Figure 1.
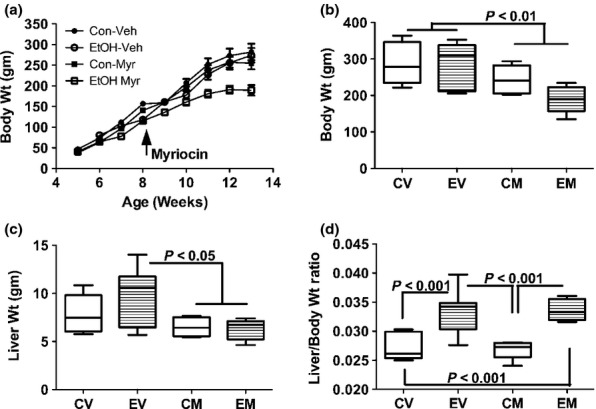
Effects of chronic ethanol feeding and myriocin treatment on body and liver weights. Adult Long Evans male rats (beginning at 5 weeks of age) were maintained for 8 weeks on isocaloric liquid diets containing 0% or 37% ethanol by caloric content. After 3 weeks on the liquid diets, rats in each group were treated with vehicle or myriocin by i.p. injection on Mondays, Wednesdays, and Fridays of the subsequent 5 weeks of the experiment. (a) Rats were weighed weekly and (b) on the last day of the experiment. (c) Fresh livers were weighed immediately upon harvest, and (d) individual ratios of liver to body weights were calculated. Data were generated from 10 to 12 rats per group. Box plots depict medians (horizontal bars), 95% confidence intervals (upper and lower limits of boxes), and ranges (stems). Inter-group comparisons were made by repeated measures one-way anova with post-hoc Tukey tests of significance. CV, control diet, vehicle (saline) injected; EV, ethanol diet, vehicle treated; CM, control diet, myriocin treated; EM, ethanol diet, myriocin treated.
