Figure 7.
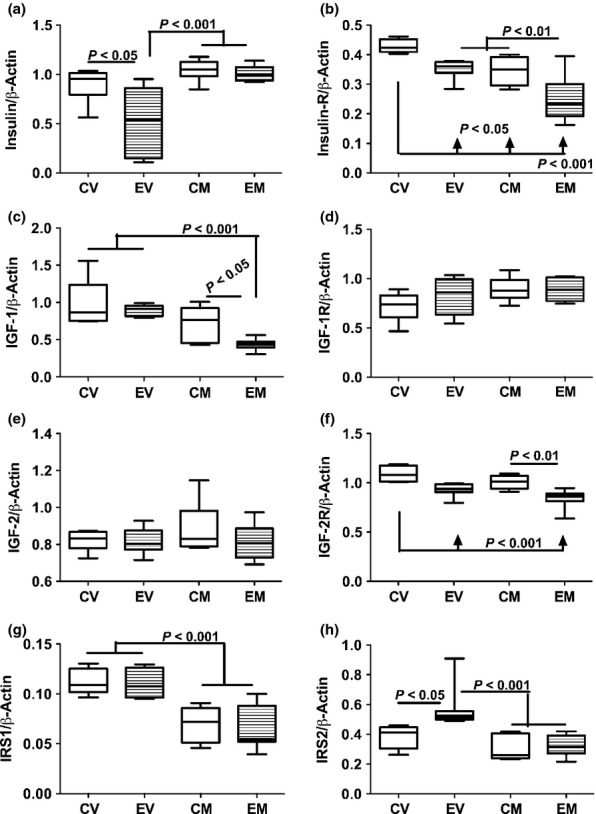
Chronic ethanol feeding and myriocin treatment effects on hepatic insulin, IGF and IRS signaling mechanisms. Total RNA was isolated from livers of control and ethanol-fed, vehicle or myriocin treated adult rats. Gene expression was measured using by duplex qRT-PCR analysis with a probe-hydrolysis detection system. The β-actin housekeeping gene was simultaneously amplified and detected in the same well as the gene of interest (see Methods). Graphs depict relative mRNA abundance of (a) insulin polypeptide, (b) insulin receptor, (c) IGF-1 polypeptide, (d) IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R), (e) IGF-2 polypeptide, (f) IGF-2R, (g) insulin receptor substrate, type 1 (IRS1), and (h) IRS2. Box plots depict medians (horizontal bars), 95% confidence intervals (upper and lower limits of boxes), and ranges (stems). Inter-group comparisons were made by repeated measures one-way anova with post-hoc Tukey tests of significance. CV, control diet, vehicle (saline) injected; EV, ethanol diet, vehicle treated; CM, control diet, myriocin treated; EM, ethanol diet, myriocin treated.
