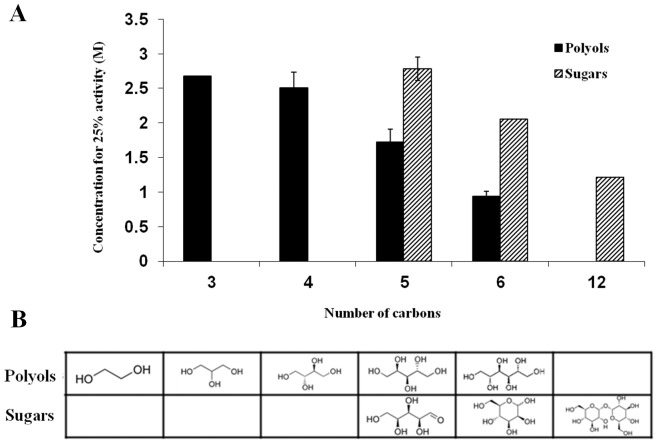
Figure 3. Comparison between the ability of sugars and polyols to protect trypsin from activity loss following heating.
(A) The concentration of various polyols and sugars that is required for restoring 25% activity of heated trypsin is presented as a function of the compounds carbon chain lengthy. (B) Examples for polyols and sugars with varying carbon chain lengths.