Figure 1.
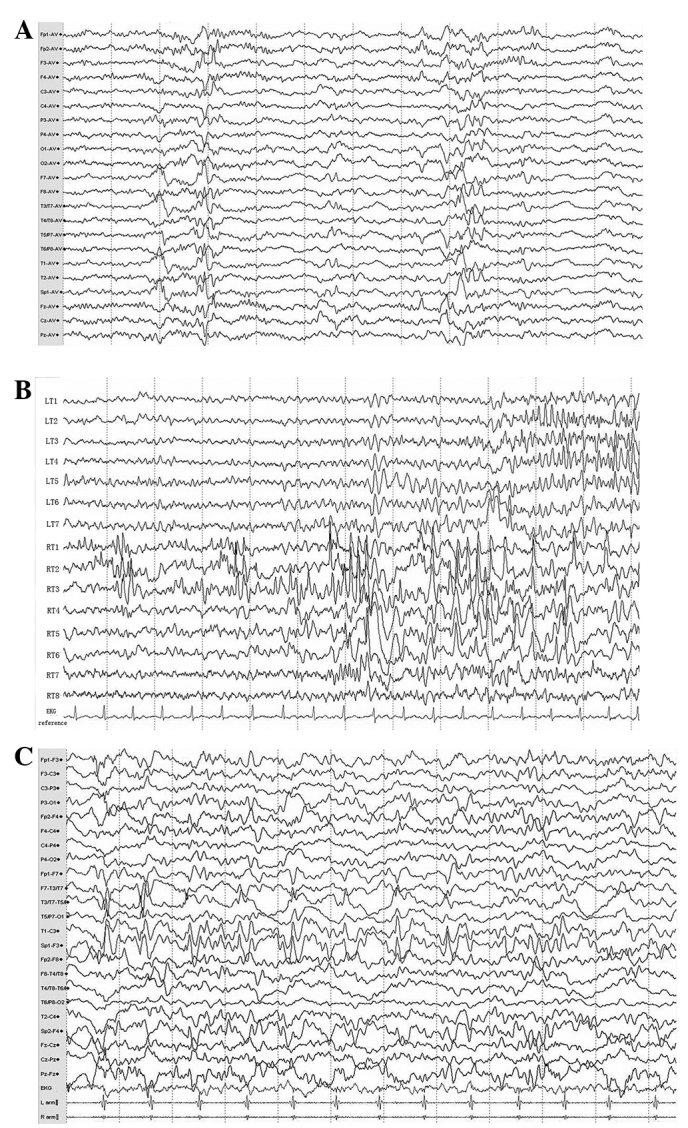
(A) Video-electroencephalogram (V-EEG) monitoring revealed intermittent multiple middle-amplitude spikes rising from the bilateral anterior temporal lobes, particularly in electrodes T1–4 (electrodes T1 and 3 were placed in the left side while T2 and 4 were in the right side). (B) The electrocorticogram (ECoG) monitoring with two depth electrodes in the bilateral temporal lobe revealed two different and independent focal seizure activities arising from the two sides of the temporal lobes as multiple spikes in the left and right temporal electrodes (LT 2–3 and RT 1–3, respectively). (C) Postoperative EEG assessment showed multiple continuous slowing and intermittent epileptiform discharges from the left sphenoid and temporal electrodes (Sp1 and T1, respectively) during the interictal period.
