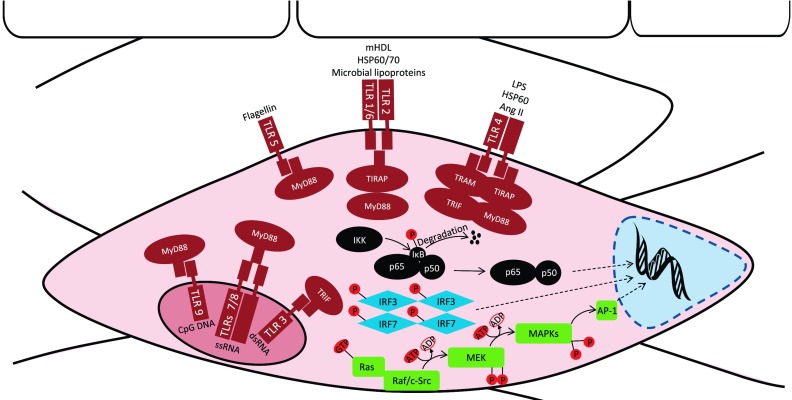
Fig. 3.
TLR ligands/DAMPs, cellular location, and signaling in the vasculature. Evolutionarily conserved similarities between TLRs on immune cells have been extended to somatic cells of the vasculature (i.e., VSMCs and ECs). TLR1, TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, and TLR6 are expressed on the plasma membrane, and TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9 are expressed on endosomal vacuoles. Activation of these receptors by DAMPs and PAMPs leads to complex cellular signaling cascades mediated by myeloid differentiation primary response protein (MyD88), Toll-IL-1 receptor (TIR)-domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon β (TRIF), TIR domain-containing adaptor protein (TIRAP), and TRIF-related adaptor molecule (TRAM). These adaptor molecules signal via MyD88-dependent or MyD88-independent pathways that result in the upregulation of pro-inflammatory mediators (cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules). The MyD88-dependent pathway includes NF-κB translocation to the nucleus to regulate inflammatory gene expression. TLR signaling activates the endogenous NF-κB inhibitor IKK complex, which phosphorylates IκB and leads to its ubiquitylation and degradation by the proteasome. IκB degradation relieves the inhibitory influence on NF-κB, and NF-κB is then able to translocate from the cytoplasm into the nucleus. MAPK regulation of pro-inflammatory mediators is also MyD88 dependent. The MAPK module contains at least 3 protein kinases in series that culminate in the activation of a multifunctional MAPK (ERK1/2, JNK/SAPK, and p38). These MAPKs subsequently result in the activation of the transcription factor activator protein (AP-1), which then translocates to the nucleus. Interferon regulatory factor (IRF)7 is also MyD88 dependent, but is only found downstream of TLR9. Phosphorylation and dimerization of IRF7 activate its translocation to the nucleus. The MyD88-independent(/TRIF-dependent) pathway downstream of TLR3 and TLR4 involves IRF3, as well as NF-κB activation. Like IRF7, IRF3 undergoes phosphorylation and dimerization for activation and translocation to the nucleus. dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; HSP, heat shock protein; mHDL, (pathophysiologically) modified HDL; ssRNA, single stranded RNA.