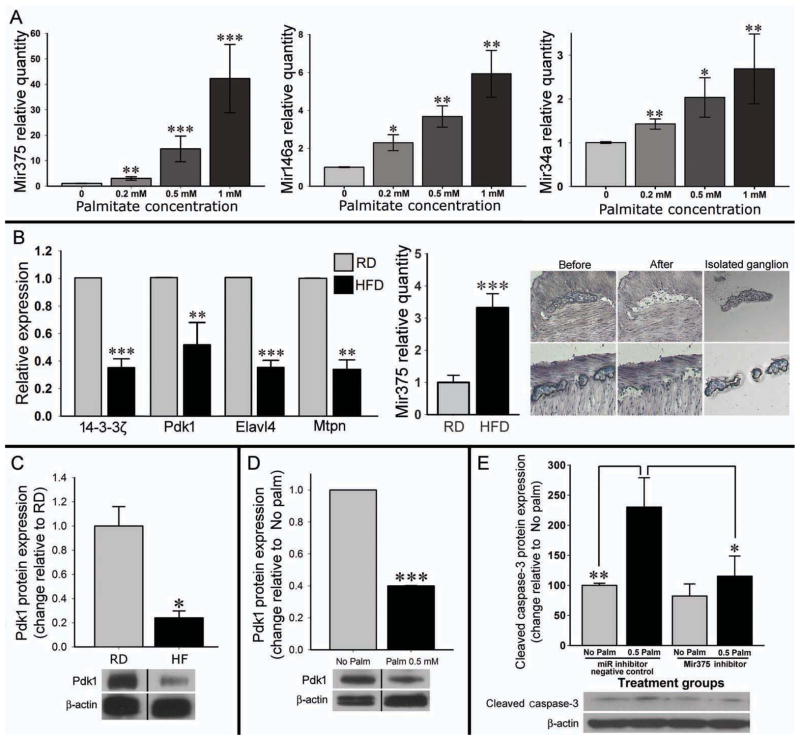
Figure 5. In vitro palmitate increases microRNA expressions and Mir375 target mRNAs decrease in myenteric ganglia of the HFD fed mice.
(A) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Mir375, Mir146a and Mir34a in the enteric neuronal cell line after treating with palmitate. (B) The expression of Mir375 and its target mRNAs in the myenteric ganglia isolated by LCM from the proximal colon of the mice treated with RD or HFD. Right panel shows how myenteric ganglion was isolated by LCM for the PCR. n= at least 3 (C) The decrease in Pdk1 mRNA in myenteric neurons was associated with a significant decrease in the protein level of Pdk1 protein in the proximal colon. (D) Similar decrease was observed in the Pdk1 protein level after palmitate treatment in enteric neuronal cells. (E) In vitro Mir375 inhibitor prevents the detrimental effect of palmitate as evident by preventing the increase of Cleaved caspase-3 in neuronal cells. HFD indicates high-fat diet; RD, regular diet. Results presented as mean ± SEM, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.