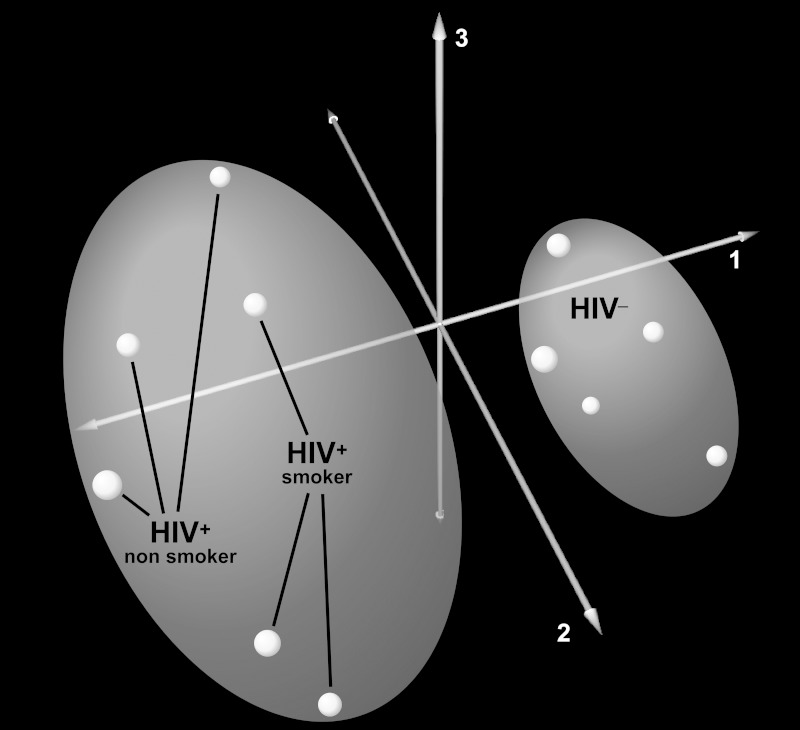
Fig. 1.
Principal component analysis (PCA) of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) proteome in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-positive (HIV+, magenta, red) HIV-negative (HIV−, cyan) subjects. PCA segregated HIV+ and HIV− subjects based on the variability across all 318 unique proteins detected in BALF, implying that HIV infection induces global changes in airspace protein expression. The first 3 components capturing the largest variance in protein expression (76.3%) are shown.