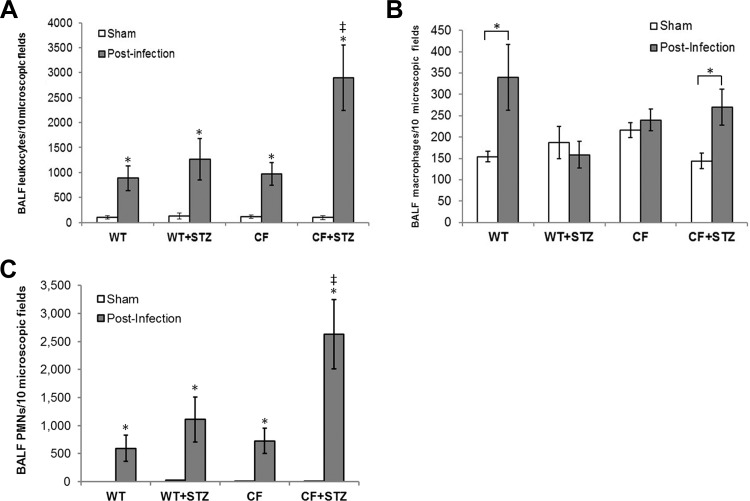
Fig. 3.
Pulmonary leukocytic infiltrate levels following Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PAO1) instillation. Data are presented as the means ± SE of positively identified leukocytes in 10 high-powered fields following differential staining. A: relative leukocytic infiltrates in BALF from sham and infected mice. PAO1 infection caused a significant increase in leukocyte infiltration compared with basal levels of leukocytes in sham-operated controls of both genotypes (*P < 0.05; n = 8–12). PAO1-infected diabetic CFKO mice showed statistically higher levels of leukocytic infiltration compared with infected WT, diabetic WT, and CFKO mice (*P < 0.05). B: pulmonary macrophage levels in the BALF. BALF macrophage levels were increased by ∼2-fold following infection with PAO1 in WT mice (*P < 0.05) but not in diabetic WT mice. Macrophages in CFKO mice were not higher than in WT mice but were higher in diabetic CFKO mice (*P < 0.05). C: polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs, neutrophils) in the BALF. PMNs increased in each group with infection (*P < 0.05). The relative increase in total leukocytic infiltration is primarily a consequence of an increase of PMNs in the BALF, constituting upwards of 90% of the total infiltrate. *Statistical difference (P < 0.05) between sham and postinfection mice within each group. ‡Statistical difference (P < 0.05) between diabetic CFKO and other groups.