Figure 2.
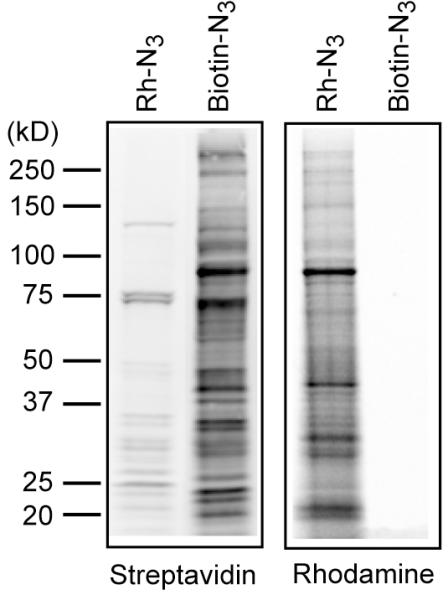
Comparison of biotin-azide detection and rhodamine-azide detection of 17-ODYA labeling. BW5147 cells were metabolically labeled with 17-ODYA for 4 hours, then lysed and the insoluble fraction was reacted with either 20 μM rhodamine-azide or 400 μM biotin-azide. The resulting samples were separated using a 4–20% Tris-Glycine SDS precast mini-gel. The gel was first scanned using a Hitachi FMBioII flatbed fluorescence scanner to detect rhodamine fluorescence. The gel was then transferred to nitrocellulose, blocked with 5% BSA, and probed with Streptavidin 800 (LiCOR), and scanned using a LiCOR fluorescence scanner. The gel demonstrates the relative sensitivity of both approaches for detection.
