Abstract
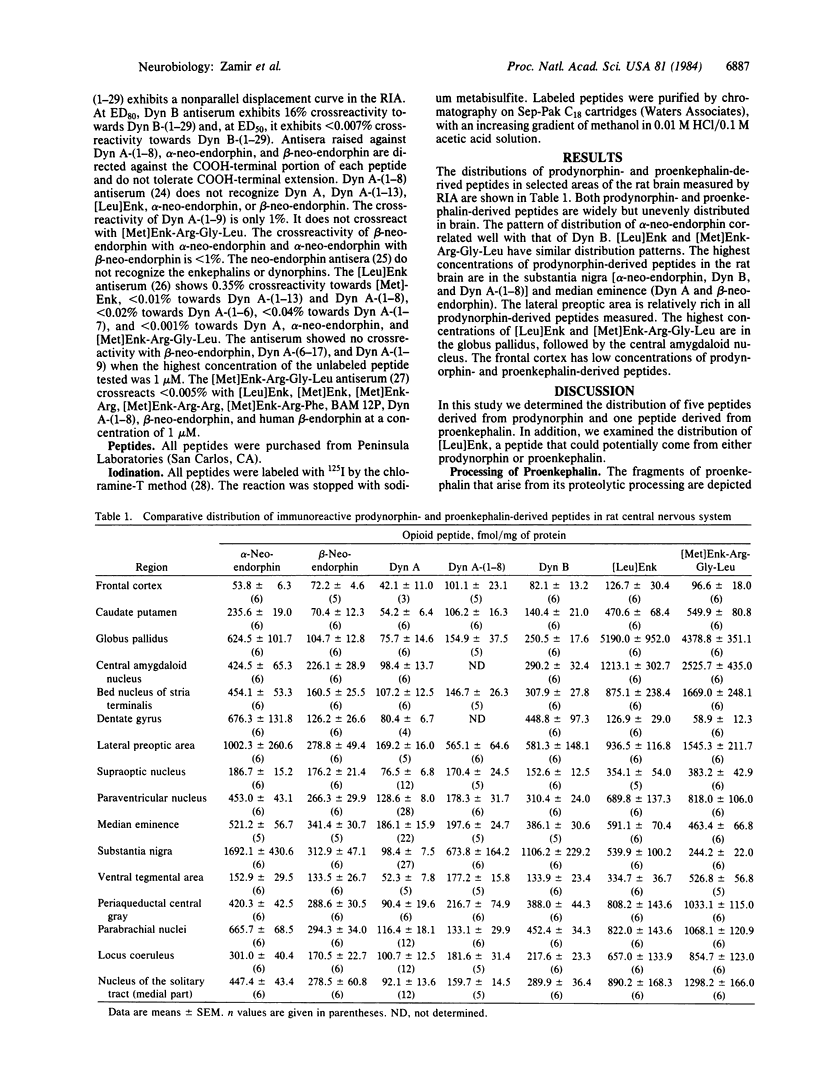
Prodynorphin-derived peptides [dynorphin A (Dyn A)-(1-17), Dyn A-(1-8), Dyn B, alpha-neo-endorphin, and beta-neo-endorphin] and proenkephalin-derived peptides [[Leu]enkephalin [( Leu]Enk) and [Met]enkephalin-Arg6-Gly7-Leu8 [( Met]Enk-Arg-Gly-Leu]) in selected brain areas of the rat were measured by specific radioimmunoassays. We report here that different regions of rat brain contain strikingly different proportions of the prodynorphin and proenkephalin-derived peptides. There is a molar excess of alpha-neo-endorphin-derived peptides over Dyn B and Dyn A-derived peptides in many brain areas. [Leu]Enk concentrations exceed those of [Met]Enk-Arg-Gly-Leu in certain brain areas such as the substantia nigra, dentate gyrus, globus pallidus, and median eminence (areas rich in dynorphin-related peptides). These results indicated that (i) there is differential processing of prodynorphin in different brain regions and (ii) [Leu]Enk may be derived from Dyn A or Dyn B (or both). In certain brain regions [Leu]Enk may derive from two separate precursors (prodynorphin and proenkephalin) in two distinct neuronal systems.
Full text
PDF
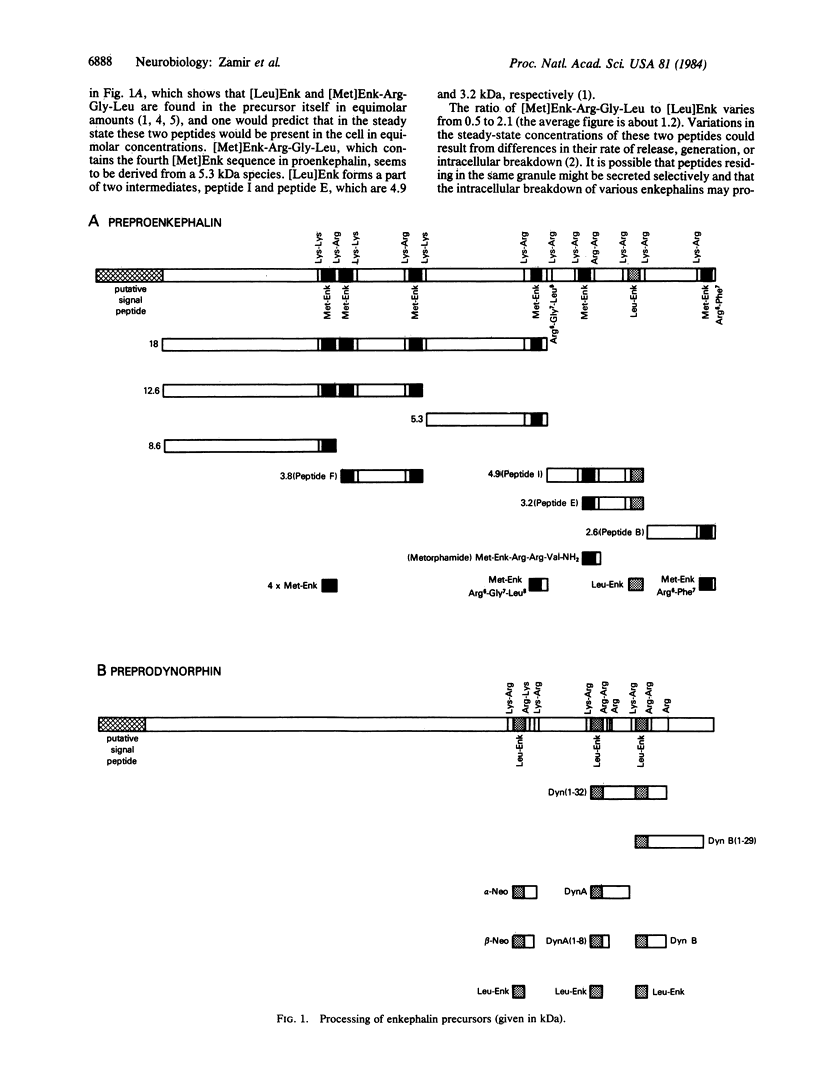

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom F., Battenberg E., Rossier J., Ling N., Guillemin R. Neurons containing beta-endorphin in rat brain exist separately from those containing enkephalin: immunocytochemical studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1591–1595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazarossian V. E., Chavkin C., Goldstein A. A specific radioimmunoassay for the novel opioid peptide dynorphin. Life Sci. 1980 Jul 7;27(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Fischli W., Lowney L. I., Hunkapiller M., Hood L. Porcine pituitary dynorphin: complete amino acid sequence of the biologically active heptadecapeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7219–7223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Seeburg P., Hoffman B. J., Gage L. P., Udenfriend S. Molecular cloning establishes proenkephalin as precursor of enkephalin-containing peptides. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):206–208. doi: 10.1038/295206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. Biogenesis, release and inactivation of enkephalins and dynorphins. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jan;39(1):17–24. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakidani H., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Noda M., Morimoto Y., Hirose T., Asai M., Inayama S., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for porcine beta-neo-endorphin/dynorphin precursor. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):245–249. doi: 10.1038/298245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangawa K., Minamino N., Chino N., Sakakibara S., Matsuo H. The complete amino acid sequence of alpha-neo-endorphin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 15;99(3):871–878. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91244-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian H., Watson S. J., Lewis M. E., Coy D., Goldstein A., Akil H. Dynorphin immunocytochemistry in the rat central nervous system. Peptides. 1982 Nov-Dec;3(6):941–954. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(82)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. L., Wahlstrom A., Lahm H. W., Blacher R., Udenfriend S. Rimorphin, a unique, naturally occurring [Leu]enkephalin-containing peptide found in association with dynorphin and alpha-neo-endorphin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6480–6483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Inoue A., Kita T., Nakamura M., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Numa S. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA for bovine corticotropin-beta-lipotropin precursor. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):423–427. doi: 10.1038/278423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Hirose T., Inayama S., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for bovine adrenal preproenkephalin. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):202–206. doi: 10.1038/295202a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palkovits M. Isolated removal of hypothalamic or other brain nuclei of the rat. Brain Res. 1973 Sep 14;59:449–450. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. G. beta-Endorphin and related peptides in pituitary, brain, pancreas and antrum. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jan;39(1):25–30. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Kilpatrick D. L. Biochemistry of the enkephalins and enkephalin-containing peptides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Mar;221(2):309–323. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S. R., Hökfelt T., Christensson I., Terenius L. Dynorphin-immunoreactive neurons in the central nervous system of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Nov 30;33(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. J., Khachaturian H., Akil H., Coy D. H., Goldstein A. Comparison of the distribution of dynorphin systems and enkephalin systems in brain. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1134–1136. doi: 10.1126/science.6128790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Barchas J. D. Immunohistochemical distribution of dynorphin B in rat brain: relation to dynorphin A and alpha-neo-endorphin systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1125–1129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Evans C. J., Barchas J. D. Predominance of the amino-terminal octapeptide fragment of dynorphin in rat brain regions. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):77–79. doi: 10.1038/299077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Evans C. J., Chang J. K., Barchas J. D. Brain distributions of alpha-neo-endorphin and beta-neo-endorphin: evidence for regional processing differences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 16;108(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91834-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Geis R., Voigt K. H., Barchas J. D. Levels of pro-neo-endorphin/dynorphin-derived peptides in the hypothalamo-posterior pituitary system of male and female Brattleboro rats. Brain Res. 1983 Jan 31;260(1):166–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90781-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Roth K. A., Evans C. J., Chang J. K., Barchas J. D. Immunohistochemical localization of dynorphin (1-8) in hypothalamic magnocellular neurons: evidence for absence of proenkephalin. Life Sci. 1982 Oct 18;31(16-17):1761–1764. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir N., Palkovits M., Brownstein M. J. Distribution of immunoreactive beta-neo-endorphin in discrete areas of the rat brain and pituitary gland: comparison with alpha-neo-endorphin. J Neurosci. 1984 May;4(5):1248–1252. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-05-01248.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir N., Palkovits M., Brownstein M. J. Distribution of immunoreactive dynorphin A1-8 in discrete nuclei of the rat brain: comparison with dynorphin A. Brain Res. 1984 Jul 30;307(1-2):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90460-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir N., Palkovits M., Brownstein M. J. Distribution of immunoreactive dynorphin in the central nervous system of the rat. Brain Res. 1983 Nov 28;280(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir N., Palkovits M., Brownstein M. J. The distribution of immunoreactive alpha-neo-endorphin in the central nervous system of the rat. J Neurosci. 1984 May;4(5):1240–1247. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-05-01240.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir N., Palkovits M., Weber E., Brownstein M. J. Distribution of immunoreactive dynorphin B in discrete areas of the rat brain and spinal cord. Brain Res. 1984 May 21;300(1):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91346-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir N., Palkovits M., Weber E., Mezey E., Brownstein M. J. A dynorphinergic pathway of Leu-enkephalin production in rat substantia nigra. Nature. 1984 Feb 16;307(5952):643–645. doi: 10.1038/307643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


