Figure 1.
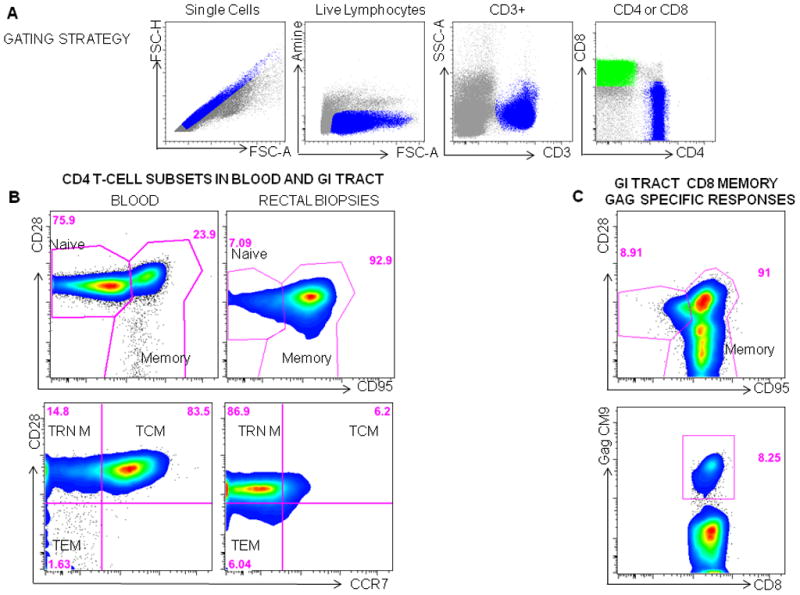
Measuring T-cell Phenotype in macaques. A Gating strategy: Mononuclear cells are first gated on single cells, then live lymphocytes or cells that are negative for the Amine dye are gated, followed by gating CD3+ T cells and then CD8+(green) and CD4+ (blue) subsets. B. Four CD4 T cell populations can be identified in the blood or rectum in macaques using CD28, CD95 and CCR7. First naïve (CD28+CD95−) cells and memory (CD95+CD28+/−) cells are gated. The memory population can then be differentiated by CD28 and CCR7 into central memory cells (TCM:CD28+CCR7+), transitional memory (TRN M: CD28+CCR7−) and effector/effector memory cells (TEM: CD28−CCR7−)cells. C Mononuclear cells isolated from rectal biopsies obtained from a vaccinated SIV infected animal, 10 days post SIV infection are gated using the strategy shown in A, CD8 memory T cells are then gated (CD95+CD28+/−) and the frequency of SIV Gag specific memory cells to the CM9 epitope are determined using an MHC Pentamer.
