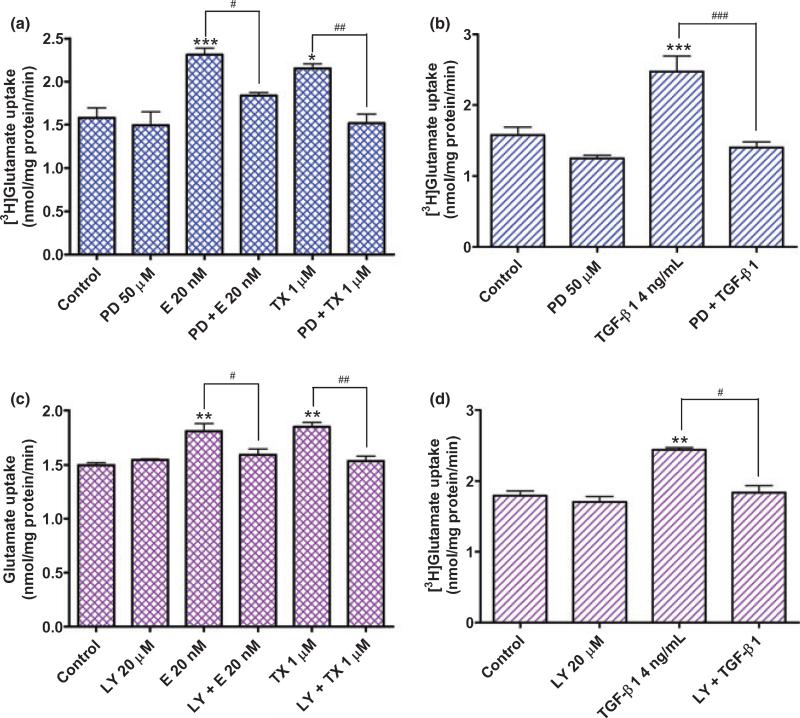
Fig. 10.
(a,b) Activation of the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway is required for both E2/TX(a)- and TGF-β1(b)-induced enhancement of glutamate uptake in astrocytes. The addition of PD98059 50 μM, an inhibitor of MAPK/ERK, to the culture media 30 min prior to E2/TX or TGF-β1 treatment for 24 h abolished the E2/TX- or TGF-β1-induced enhancement of glutamate uptake (PD98059 was dissolved in DMSO as a concentration of 6.5 mg/mL and diluted with Opti-MEM experimental media). (c,d) Activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is required for both E2/TX(c)- and TGF-β1(d)-induced enhancement of glutamate uptake in astrocytes. The addition of LY294002 20 μM, an inhibitor of PI3K/Akt, to the culture media 30 min prior to E2/TX or TGF-β1 treatment for 24 h abolished the E2/TX- or TGF-β1-incuded enhancement of glutamate uptake (LY294002 was dissolved in DMSO at a concentration of 25 mg/mL and diluted with Opti-MEM media). The same concentration of DMSO was used as a control. (#p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. control; Tukey's test following anova). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 4).