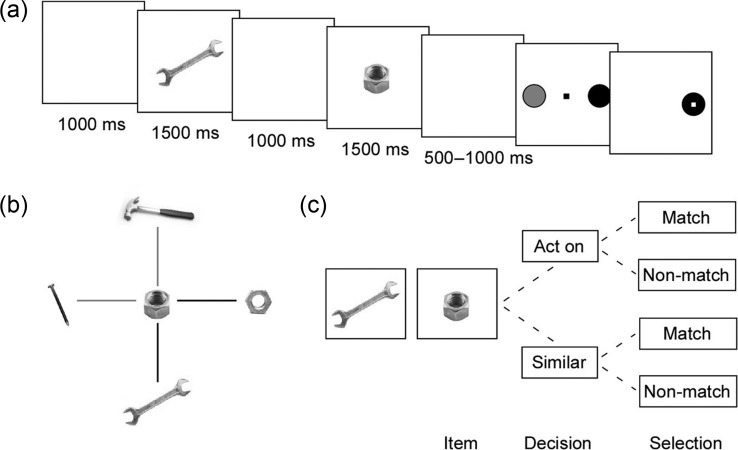
Figure 1.
Behavioral task. (a) Subjects viewed 2 sequentially presented images (1500msec each) an intervening fixed delay (1000msec). After a variable second delay (500–1000msec), they were shown a red and green target randomly positioned on either side of the screen. They then used a joystick to move a cursor to the green target to indicate that the images matched or to the red target to indicate that they did not. Images could match either as a compatible TO pair (e.g. wrench–nut, as depicted here) or as 2 items similar in identity (e.g. wrench–wrench or nut–nut). (b) Sample permutation of possible item combinations with a nut. Black bars represent matches, and gray bars nonmatches. (c) Evaluation paradigm for a sample item pair. Subjects first decided whether to invoke the act on or similar rule and then judged the pair to be either matching or nonmatching under the selected rule.