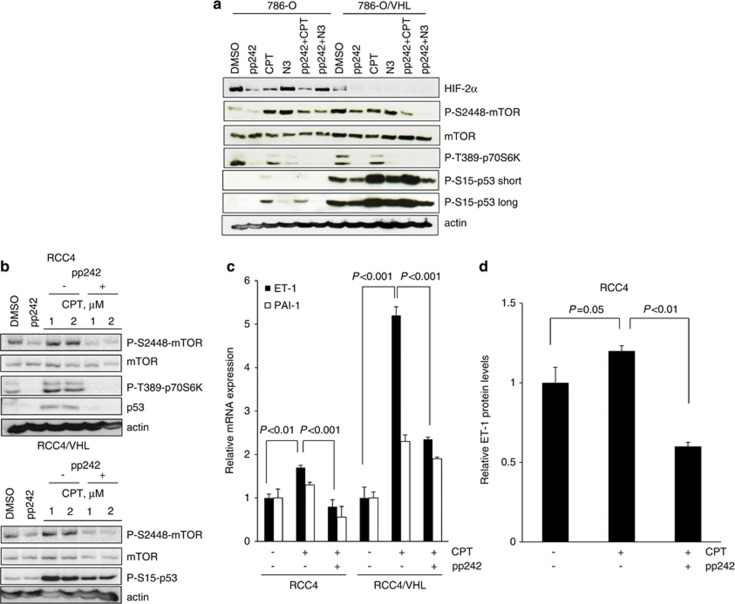
Figure 7.
Attenuation of mTORC1/2 kinase ablates CPT-induced p53- and p53-dependent responses in ccRCC. (a) The 786-O and 786-O/VHL cells were treated with 400 nM pp242, 2 μM CPT, 10 μM nutlin-3a (N3) or vehicle control (DMSO) alone for 24 h, or preincubated with 400 nM pp242 for 1 h before addition of 2 μM CPT or 10 μM N3 for a further 24 h. Whole-cell lysates were assayed by western blot for HIF-2α, mTOR, phosphorylated p53 (S15), mTOR (S2448) and p70S6K (T389) proteins. Actin was used as a loading control. Short and long exposure times are shown for P-S15-p53. (b) RCC4 and RCC4/VHL cells were treated with 400 nM pp242 or vehicle control (DMSO) alone or preincubated with 400 nM pp242 for 1 h before addition of either 1 μM or 2 μM CPT for 24 h. Whole-cell lysates were assayed by western blot for mTOR, p53, phosphorylated p53 (S15), mTOR (S2448) and p70S6K (T389) proteins. Actin was used as a loading control. (c) RCC4 and RCC4/VHL cells were preincubated with 400 nM pp242 for 1 h before addition of 2 μM CPT for 24 h and mRNA expression of ET-1 and PAI-1 were assessed by real-time quantitative PCR relative to GAPDH. Mean±S.E. of duplicate values of one representative experiment is shown. (d) RCC4 cells were pretreated with 400 nM pp242 for 1 h before addition of 2 μM CPT for 24 h. Conditioned media were harvested and assessed for secreted ET-1 protein levels by ELISA and normalized to total protein levels. Mean±S.E. of duplicate values of one representative experiment is shown