Figure 3.
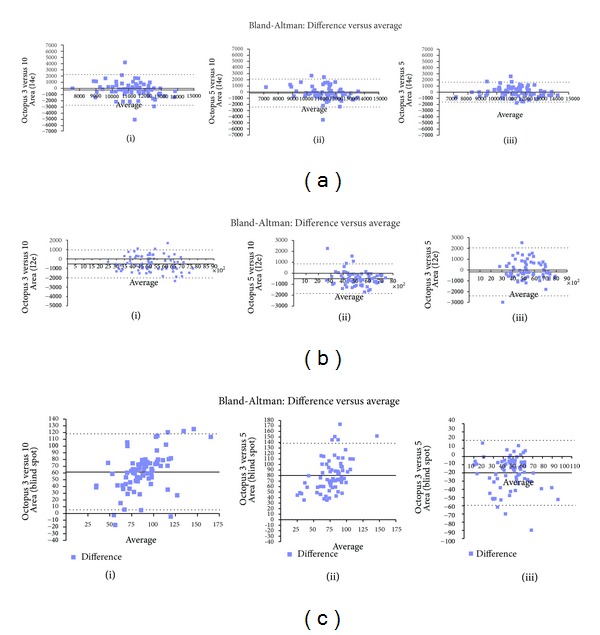
(a) Bland-Altman analysis: I4e peripheral area. (i) The dotted lines represent ±1.96SD with limits of agreement of −2731 to 2239. The solid line represents the mean bias of −246.17 degrees2. (ii) The dotted lines represent ±1.96SD with limits of agreement of −2433 to 2110. The solid line represents the mean bias of −161.54 degrees2. (iii) The dotted lines represent ±1.96SD with limits of agreement of −1601 to 1631. The solid line represents the mean bias of −15.24 degrees2. There is good correlation with distribution of differences across increasing average close to mean bias and within limits of agreement. (b) Bland-Altman analysis: I2e stimulus area. (i) The dotted lines represent ±1.96SD with limits of agreement of −2029 to 943. The solid line represents the mean bias of −542.81 degrees2. (ii) The dotted lines represent ±1.96SD with limits of agreement of −1825 to 852. The solid line represents the mean bias of −486.45 degrees2. The comparison of isopter area using different speeds is significant (P = 0.001). There is no correlation between areas obtained using different stimulus speeds with variability noted across all comparisons. (iii) The dotted lines represent ±1.96SD with limits of agreement of −1694 to 1596. The solid line represents the mean bias of −48.95 degrees2. (c) Bland-Altman analysis: I4e blind spot stimulus area. (i) The dotted lines represent ±1.96SD with limits of agreement of 5 to 117. The solid line represents the mean bias of 61.46 degrees2. The comparison of isopter area using different speeds is significant (P = 0.001). There is no correlation between areas obtained using different stimulus speeds with variability noted across all comparisons. (ii) The dotted lines represent ±1.96SD with limits of agreement of 22 to 138. The solid line represents the mean bias of 80.25 degrees2. The comparison of isopter area using different speeds is significant (P = 0.001). There is no correlation between areas obtained using different stimulus speeds with variability noted across all comparisons. (iii) The dotted lines represent ±1.96SD with limits of agreement of −59 to 20. The solid line represents the mean bias of −19.87 degrees2. The comparison of isopter area using different speeds is significant (P = 0.001). There is no correlation between areas obtained using different stimulus speeds with variability noted across all comparisons.
