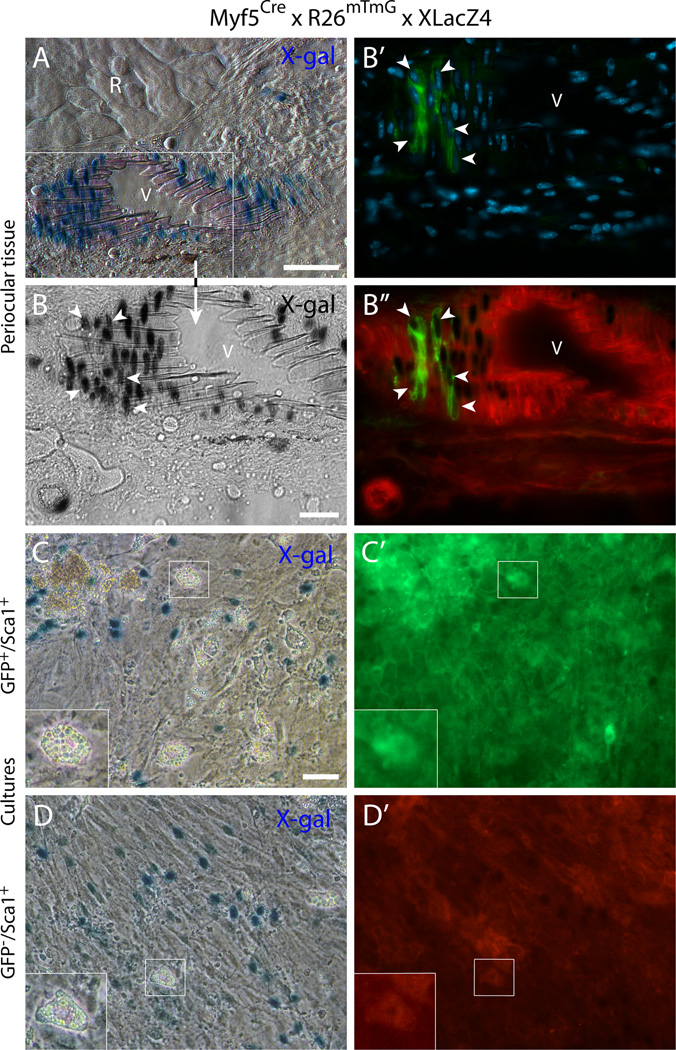
Fig. 6. Histological and cell culture analyses of the double reporter mouse Myf5Cre × R26mTmG × XLacZ4 establish a connection between the vascular-associated (Myf5Cre-driven) GFP+ cells and the mural cell marker XLacZ4.
(A-B”) Cross-section from periocular preparation at the level of the optic nerve, immediately posterior to the eye, depicting (A) X-gal+- cells at the wall of a blood vessel close to a rectus muscle and (B-B”) a higher magnification view of the same blood vessel, identifying DAPI-stained cells at the vessel wall that co-express nuclear β-gal and GFP (white arrowheads). R, rectus muscleV, blood vessel. (C-D’) Representative images of day 14 cultures of (C-C’) GFP+/Sca1+ cells and (D-D’) GFP/Sca1+ cells after staining with X-gal. The two populations, isolated from EOM preparations, were sorted by FACS from G0-G1 cells after depletion of CD31+ and CD45+ cells. Inserts in the lower left corner of (C) and (D) represent higher magnification views of the regions delineated by a white box in each corresponding panel, depicting adipogenic cells that develop spontaneously in these cultures with time. Scale bars in (A) and (C), 50µm, and in (B), 25µm.