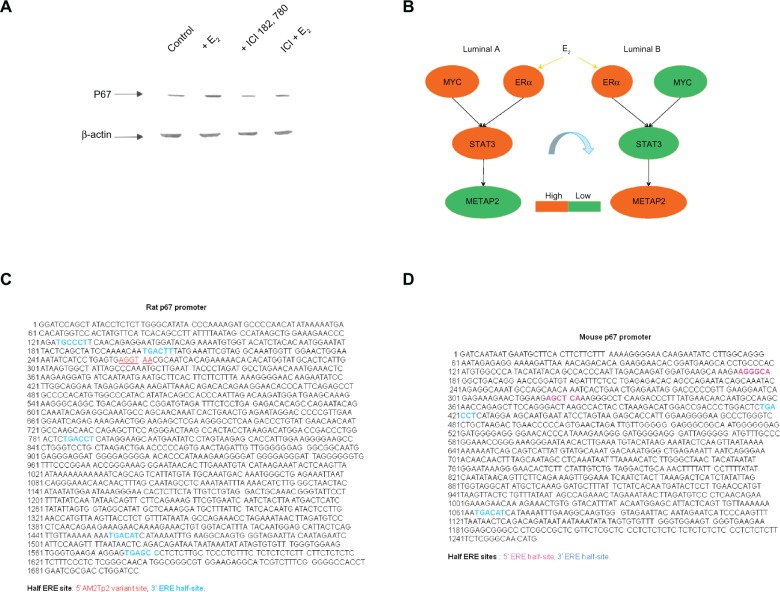
Figure 5.
In vitro validation of an ERα target gene—METAP2 (p67).
The upper left panel shows the results of western blot analysis on protein expression levels of METAP2 (p67) in MCF-7 cell model (A).
Western blot analysis for METAP2 encoded protein indicates it to be regulated by ERα. We found increased p67 protein in MCF-7 with E2 treatment as compared to that with fulvestrant (ICI 182, 780 or ICI) treatment, (ICI + E2) treatment and control. MCF-7 cells were deprived of estrogen for 2 days and treated with 10−9 M E2 (labeled as + E2), 10−7 M ICI183,780 (labeled as + ICI183,780), or a combination of both (ICI + E2) for 48 hours. Total lysate (60 μg/lane) from MCF-7 cells was resolved in 7.5% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-rat p67. β-actin was as the loading control. The lower blot was probed with anti-β-actin. The upper right panel shows that a diagram of the network prediction for interaction between ERα and STAT3 results in a switch in expression mode of their potential target gene-METAP2, which is predicted to be subtype relevant in ER(+) IDCs (B).
Moreover, METAP2 is predicted to be shared target genes due to the combinatorial interaction of 2 given transcription factors (see the overlapping network of MYCnSTAT3 and ESR1nSTAT3 in Table S2.4 of Suppl. 2) but it is neither in the overlapping network of ESR1 and STAT3 nor in that of MYC and STAT3 (Table S2.6 in Suppl. 2). Based on the network analysis results, the proposed interplay between promoter use pathways of ESR1 nSTAT3 and MYCnSTAT3 in luminal A and B in regulating METAP2 is proposed (B).
The lower left panel demonstrates that DNA sequence of promoter region for rat METAP2 (p67) (GenBank: U37710) includes 5 3′ ERE half-sites45 and a 5′Am2Tp2 variant site46 (C). This indicates rat METAP2 to be a target gene of ERα due to the half-ERE sites to be the candidate binding sites of ERα.
The lower right panel demonstrates that DNA sequence of promoter region for mouse METAP2 (p67) includes two 5′ ERE half-sites and two 3′ ERE half-sites (D). This indicates mouse METAP2 to be a target gene of ERα due to the half-ERE sites to be the candidate binding sites of ERα.