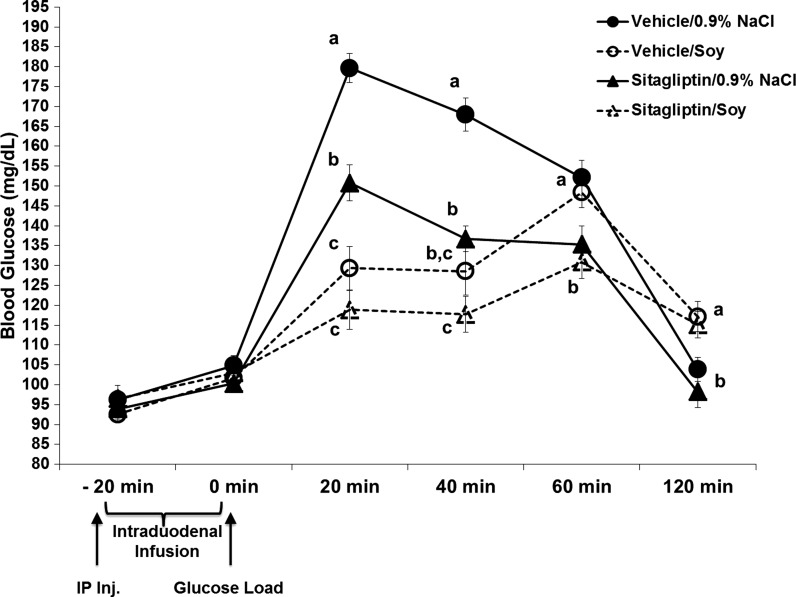
Fig. 3.
Blood glucose concentrations (mg/dl) following intraperitoneal injection of vehicle or sitagliptin (6 mg/kg; time −20 min) in combination with intraduodenal infusions of 4 kcal of soy protein or 0.9% NaCl in an oral glucos-tolerance test (2 g/kg of 25% glucose delivered via gavage at time 0). Sitagliptin alone significantly suppressed blood glucose levels compared with vehicle-saline at 20, 40, and 60 min postglucose load. Soy protein alone significantly suppressed blood glucose levels compared with vehicle-saline at 20 and 40 min postglucose load. The combination of sitagliptin and soy protein did not produce any significant enhancement in the glycemic suppressive effects from either treatment alone. Within a time point, data points with different letters are significantly different from each other (P < 0.05). Data are means ± SE.