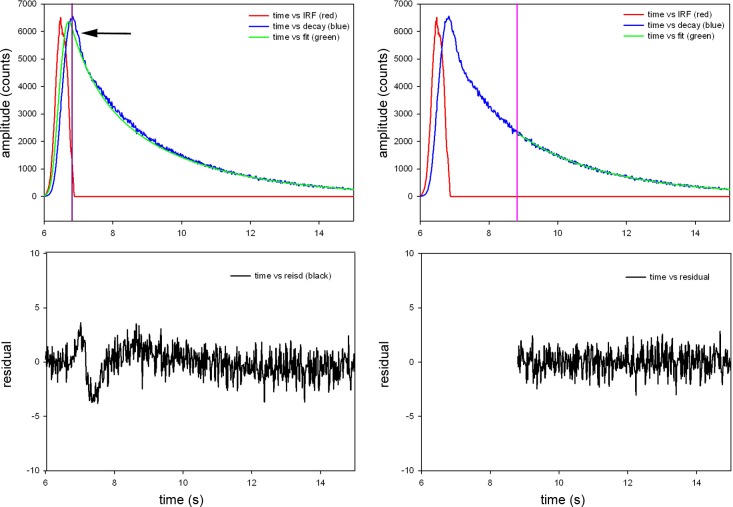
Fig. 2.
Fluorescence decay of parallel polarized light from rigor myofibril. A: no gate applied, i.e., the signal collection is started at the peak of the signal (violet line) and continued through the complete fluorescence decay. This includes scattered light (arrow). B: the residuals have significant dip at the time corresponding to scattering of light and are not well fitted by a straight horizontal line. C: gating applied. In TCSPC systems, photons are collected one-by-one. Here, photons detected within 8.8 ns of the start of the measurement (an arbitrarily determined point in time with relation to the excitation pulse) are eliminated from our measurements. All that remains are photons collected 8.8 ns or later from the start of the measurement (indicated by the violet line). D: residuals of the gated signal are quite flat. The same procedure is applied to perpendicular polarized light.