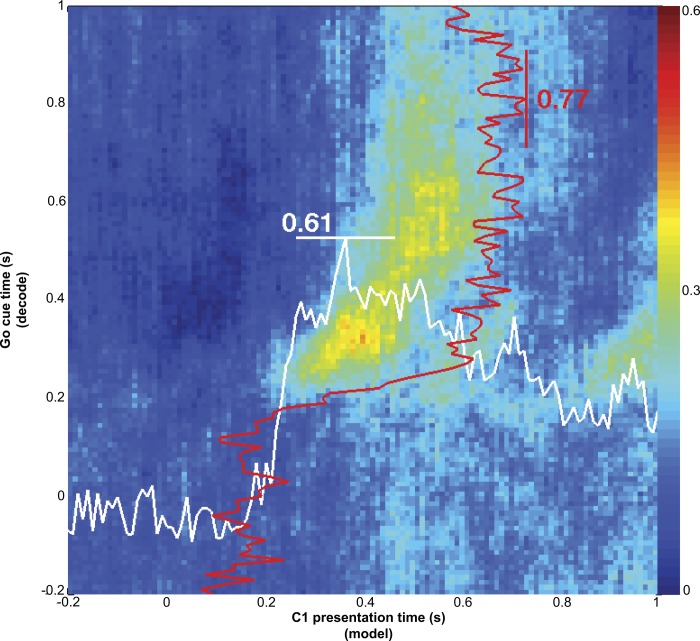
Fig. 4.
Direction coding similarity between C1 and C2 responses. An 8-way discrete classifier model [support vector machine, SVM; radial basis function (RBF) kernel] for target direction was built from bins around the time indicated on the x-axis. Target direction was decoded from bins around the time indicated on the y-axis. The color of each point represents the fraction of correctly decoded trials for the time after C2 at the y-axis using a classifier trained on data from C1 at the time on the x-axis. Also shown is the cross-validated decoding performance of the C2 responses (red lines) and C1 responses (white lines) within their respective conditions. The origin for the red and white lines at bottom left. The existence of a region of high decoding power in this cross-condition (C1 to C2) decoding scenario suggests that C1 activity (along the x-axis) and the early part of the C2 activity (along the y-axis) code cue direction similarly across the population. Red and white lines show that each condition's responses (C1 or C2) also contain direction information. The maximum decoding power within the C1 condition (white line along x-axis) is 0.61, and the maximum decoding power within the C2 condition is 0.77 (red line along y-axis).