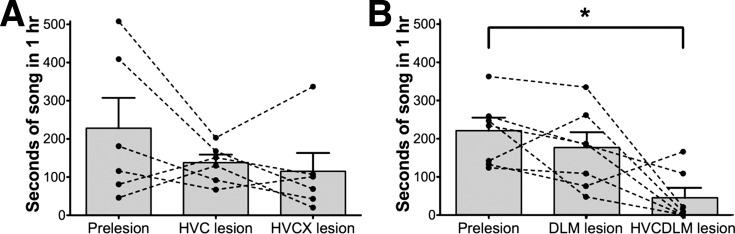
Fig. 4.
The amount of song produced by birds with HVC and DLM double lesions is dramatically reduced. A: the average amount of song produced in 1 h by 6 birds prelesion, after HVC lesions alone, and after HVC, Area X lesions [mean for each group: prelesion = 224 ± 78 s (SE); HVC-lesioned = 135 ± 20 s; HVC, X-lesioned = 113 ± 47 s]. Although there was a tendency for birds to sing less after HVC lesions, the amount of singing across birds was not significantly different between conditions (P = 0.2522, Friedman test). B: in contrast, the average amount of song produced in 1 h dropped significantly across birds after HVC, DLM lesions, although not after DLM lesions alone (mean for each group: prelesion = 215 ± 33 s; DLM-lesioned = 171 ± 39 s; HVC, DLM-lesioned = 44 ± 25 s; P = 0.0272, Friedman test; prelesion vs. HVC, DLM-lesioned, P < 0.05, Dunn's multiple-comparison posttest; n = 7 birds). *P < 0.05. Error bars indicate SE.