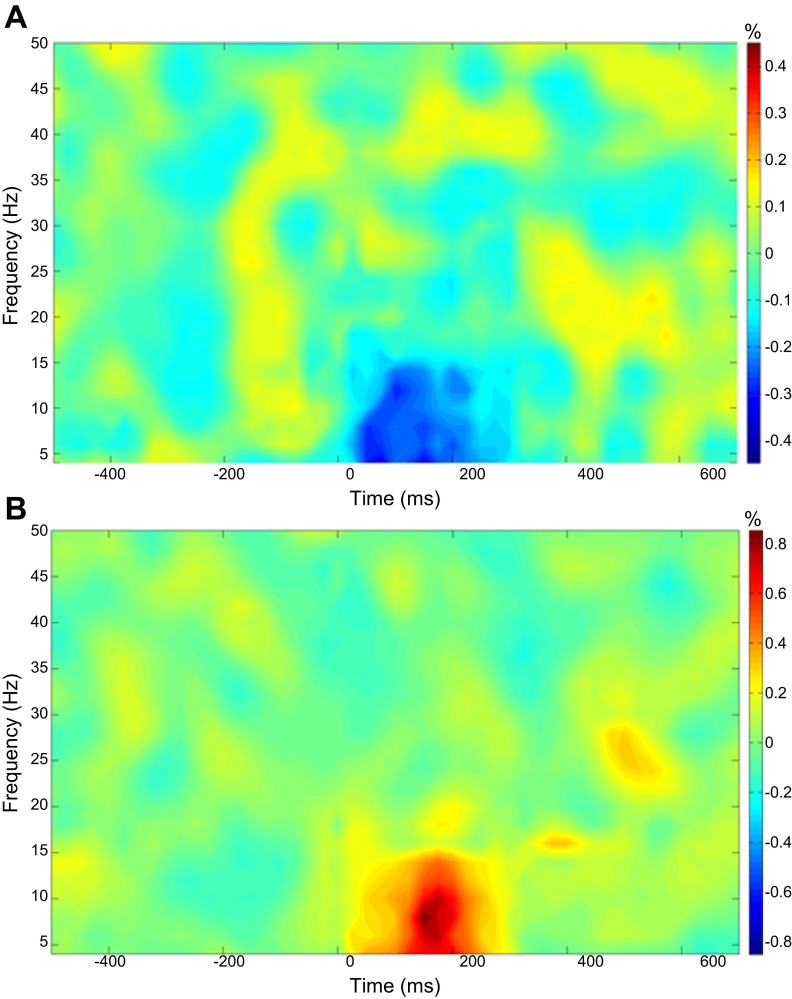
Fig. 2.
Average time-frequency spectra in controls and children with cerebral palsy (CP) during somatosensory stimulation. Time (in ms) is denoted on the x-axis, with 0 ms defined as stimulation onset. Frequency (in Hz) is shown on the y-axis. The average patterns of event-related spectral changes during the foot stimulation task, expressed as % difference from baseline (−500 to 0 ms), are shown in the children with CP (A) and the control group (B). In each case, the frontoparietal magnetoencephalography sensor with the greatest response amplitude was chosen for each participant, and these were averaged across the person's respective group. As shown, the children with CP (A) exhibited a decrease in the 4- to 14-Hz band during the 25- to 275-ms time window, whereas the healthy children showed a strong increase in this same time-frequency window (4–14 Hz, 25–275 ms). Note that the color scale for each plot is shown to the right, and that the scale for controls is two times that of the children with CP.