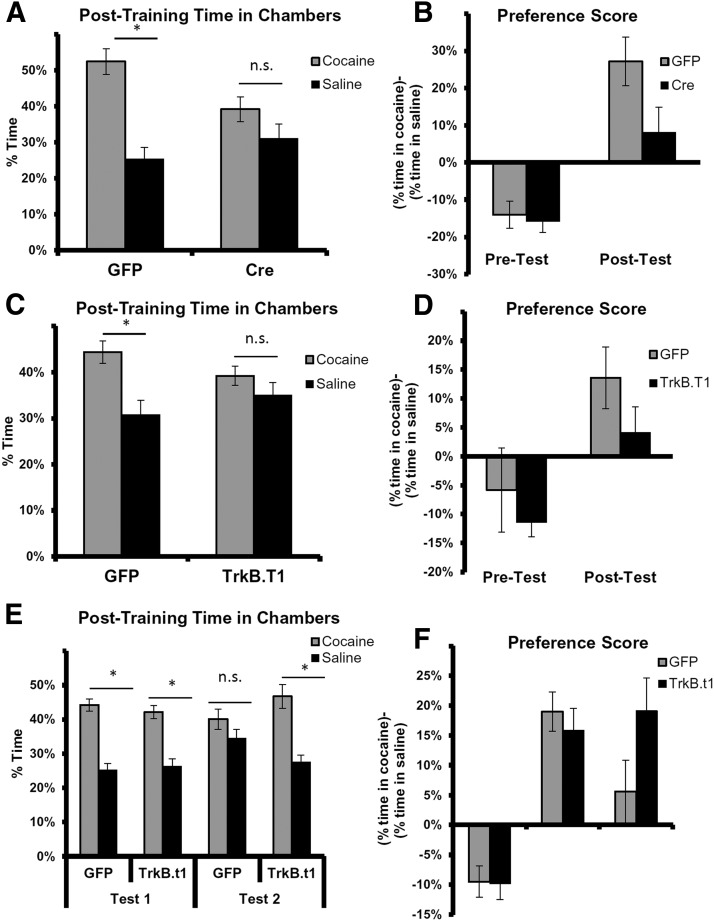
Figure 4.
Bdnf knockdown in the amygdala and dominant-negative impairment of TrkB prevent development of preference for a chamber previously paired with cocaine. A, LV-GFP mice (GFP) spent significantly more time in the cocaine-paired chamber during post-testing (F(1,14) = 17.0, p = 0.001), whereas LV-Cre mice (Cre) did not. B, In the post-test, the average LV-Cre group preference score trended lower than the average LV-GFP group score. These results suggest that LV-Cre mice showed less preference for the cocaine-paired chambers after CPP training than the control group. C, In a separate set of experiments, LV-GFP control mice spent significantly more time in the cocaine-paired chamber during post-testing (F(1,15) = 7.0, p = 0.019), whereas mice infected with LV-TrkB.t1 did not (p > 0.1). D, On the post-test, the average LV-TrkB.t1 group preference score tended lower than the average LV-GFP group score. E, In an additional set of experiments designed to examine CPP extinction, we found that both groups exhibit preference for cocaine chambers in Test 1, but only the LV-TrkB.t1-infected animals exhibit this preference in Test 2. F, This effect is further demonstrated in the relative cocaine preference in pretest, post-test 1, and post-test 2. Data are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05. n.s., not significant.