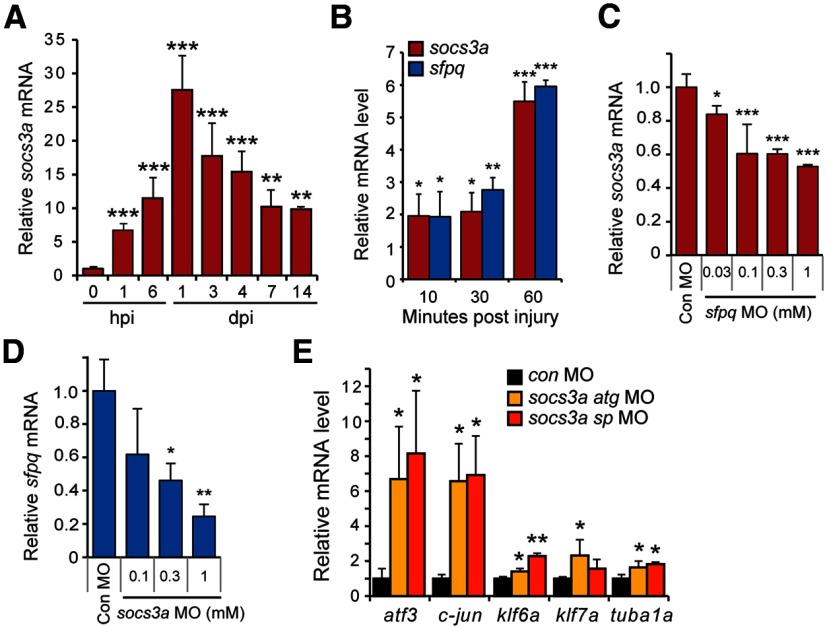
Figure 5.
socs3a and sfpq are coordinately induced and regulate each other's expression. A, qPCR analysis of socs3a mRNA induction after optic nerve lesion. RNA levels are normalized to that found in uninjured control. **p < 0.01, compared with uninjured control. ***p < 0.001, compared with uninjured control. n = 4. Error bars indicate SD. B, qPCR analysis of socs3a and sfpq mRNA induction shortly after optic nerve lesion. *p < 0.05, compared with uninjured control. **p < 0.01, compared with uninjured control. ***p < 0.001, compared with uninjured control. n = 4. Error bars indicate SD. C, qPCR shows Sfpq knockdown suppresses socs3a mRNA expression at 3 dpi. *p < 0.05, compared with control MO. ***p < 0.001, compared with control MO. n = 3. Error bars indicate SD. D, qPCR shows Socs3a knockdown suppresses sfpq mRNA expression at 3 dpi. *p < 0.05, compared with control MO. **p < 0.01, compared with control MO. n = 3. Error bars indicate SD. E, qPCR shows that Socs3a knockdown stimulates expression of regeneration-associated genes at 3 dpi. mRNA levels are normalized to those obtained with control MO-treated optic nerves. *p < 0.05, compared with control MO. **p < 0.01, compared with control MO. n = 3. Error bars indicate SD.