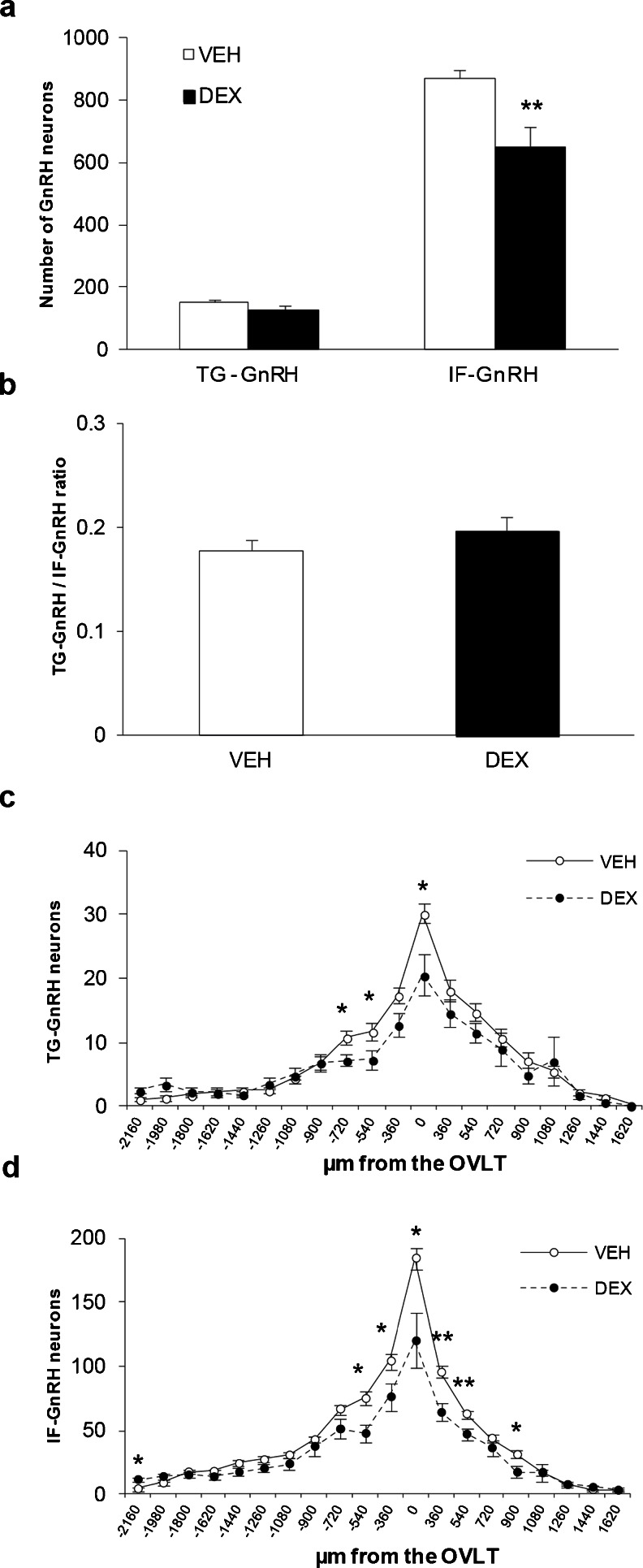
Fig. 5.
Maternal DEX exposure on number and distribution of IF-GnRH and TG-GnRH neurons in P0 male offspring. a Total number of TG-GnRH and IF-GnRH neurons in VEH-P0 (n = 10) and DEX-P0 (n = 7) males. Maternal DEX exposure decreased the total number of IF-GnRH cells in P0 males but not the TG-GnRH cells. b GnRH promoter activity expressed as Tg-GnRH/IF-GnRH neuron ratio did not differ between the VEH-P0 and DEX-P0 males. Rostral to caudal distribution of TG-GnRH (c) and IF-GnRH (d) neurons in VEH-P0 and DEX-P0 males. The TG-GnRH neurons were decreased in the OVLT and rostral to the OVLT (−540 and −720 μm from OVLT) in DEX-P0 males. Number of IF-GnRH neurons were also decreased in the OVLT, rostral (−360 and −540 μm from the OVLT) and caudal (360 and 540 μm) to the OVLT in DEX-P0 males. Data are represented by the mean ± SEM for each group. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 compared to VEH-P0 group