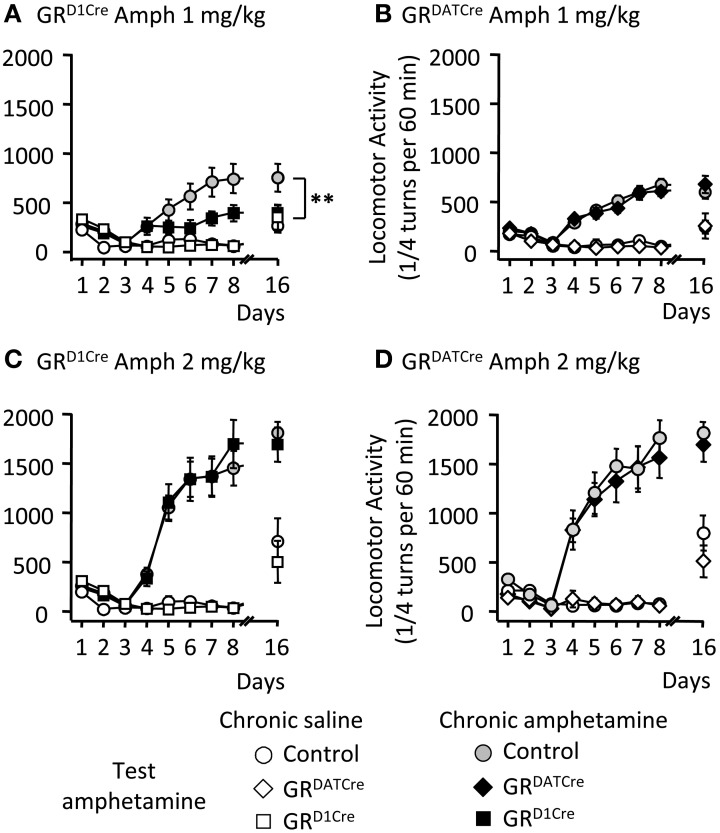
Figure 2.
The locomotor sensitization to low dose of amphetamine is selectively abolished in GRD1Cre mice. Locomotor activity is expressed as the sum of ¼ turns in a circular cylinder per hour following repeated drug or saline injections. (A) Locomotor sensitization to 1 mg/kg amphetamine daily injections in control (gray circles) and GRD1Cre mice (black squares). White circles and white squares represent control and GRD1Cre mice, respectively, which received daily injections of saline followed by a challenge injection of amphetamine 1 mg/kg on the test day. Amphetamine (1 mg/kg) induced locomotor sensitization that was abolished in GRD1Cre mice at day 16; interaction Genotype × Treatment F(1, 28) = 5.2; saline vs. drug: P < 0.01; control vs. mutant: **P < 0.01. (B) Locomotor sensitization to 1 mg/kg amphetamine daily injections in control (gray circles) and GRDATCre (black diamond) mice. White circles and white squares represent control and GRDATCre mice, respectively, which received daily injections of saline followed by a challenge injection of amphetamine 1 mg/kg following an 8-day withdrawal period. Interaction Genotype × Treatment F(1, 33) = 0.16; saline vs. drug: P < 0.001; control vs. mutant: P = 0.6. (C,D) are same than (A,B), respectively, but with 2 mg/kg amphetamine. n = 8–10 per group. (C) Interaction Genotype × Treatment F(1, 36) = 1.72; saline vs. drug: P < 0.001; control vs. mutant: P = 0.67. (D) Interaction Genotype × Treatment F(1, 37) = 0.27; saline vs. drug: P < 0.001; control vs. mutant: P = 0.21.