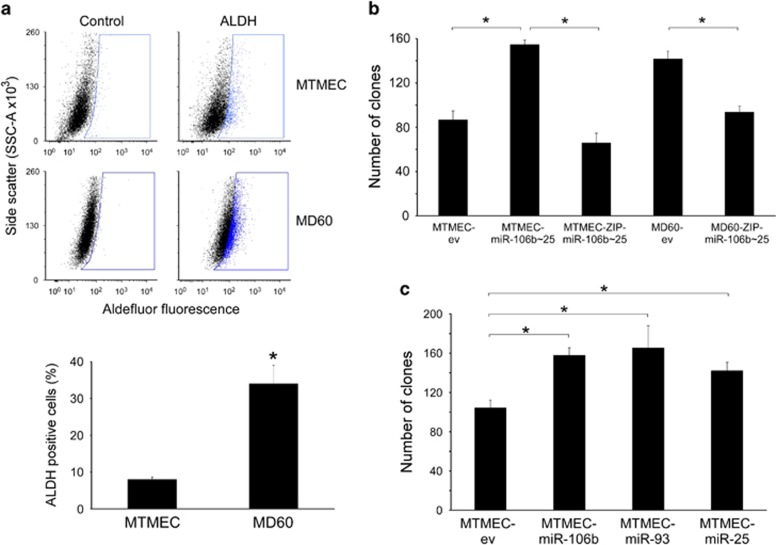
Figure 4.
The individual miRs in the miR-106b∼25 cluster have proto-oncogenic activity in breast cancer cells. (a) Doxorubicin resistance is accompanied by an increase in the percentage of ALDH-positive cells. Drug-sensitive MTMEC cells were used to generate drug-resistant derivatives able to proliferate after 24-h exposures to 60 ng/ml (MD60) of doxorubicin. For ALDH activity, cells were treated with Aldefluor alone (ALDH) or in the presence of the ALDH inhibitor diethylaminobenzaldehyde (Control) and then analyzed by flow cytometry. The blue gate was set up with the control cells to include no >1% of the population and was used to determine the percentage of ALDH-positive cells in the absence of inhibitor. Plots shown are representative of at least three independent experiments. (b and c) The individual miRs in the miR-106b∼25 cluster have proto-oncogenic activity in breast cancer cells. Anchorage independence was determined by the formation of clones in soft agar after 4 weeks. (b) MTMEC cells transfected with a lentiviral vector expressing the miR-106b∼25 cluster (MTMEC-miR-106b∼25). A ZIP anti-miR lentiviral vector was used to knock-down miR-106b∼25 cluster expression in both MTMEC and drug-resistant MD60 cells. (c) Expression of individual miRs in MTMEC cells led to the formation of similar number of anchorage-independent clones. In all cases, cells transfected with empty vectors (ev) were used as controls. Data represent the average±S.D. of at least three independent experiments (*P<0.05)