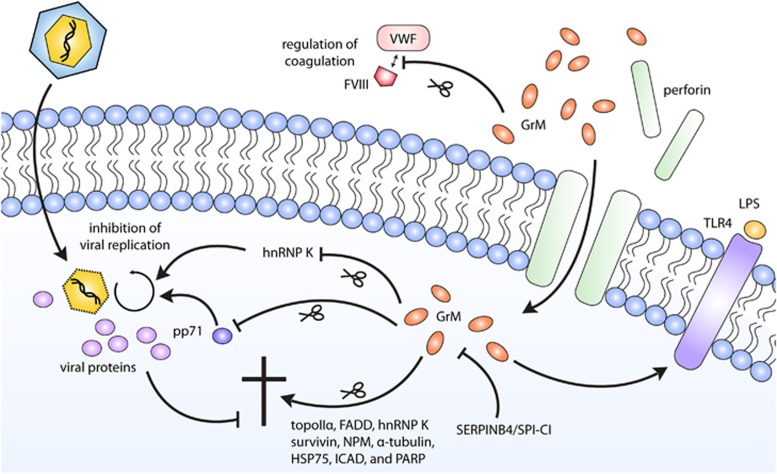
Figure 3.
The functions of GrM. After entry into a target cell via perforin-mediated pore formation in the target cell membrane, GrM can activate various signaling pathways. GrM can induce apoptosis via cleavage of a number of death substrates, among which topoIIα,32 FADD,97 hnRNP K,49 survivin,44 NPM,33 α-tubulin,47 Hsp75,45 ICAD, and PARP.46 GrM can also function in a noncytotoxic manner to inhibit HCMV replication by either cleaving the host protein hnRNP K41 or the viral protein pp71.72 In addition, GrM can stimulate LPS/TLR-4-mediated signaling via yet to be identified mechanisms.90 GrM intracellular functioning can be inhibited in tumor cells by human SERPINB492 and mouse SPI-CI.38 Next to these intracellular effects, GrM has also been found to cleave VWF, and may in that way regulate FVIII levels and coagulation91