Figure 1. Structural effect of dimerization in spinels.
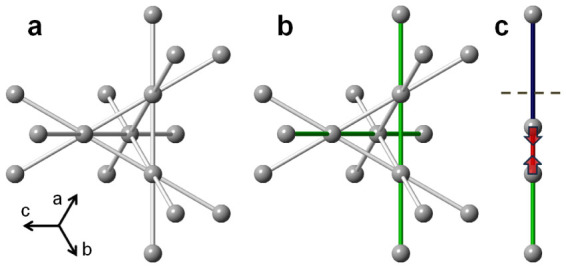
(a) Regular pyrochlore sublattice in the high temperature cubic phase of transition metal spinels. All near neighbor transition metal distances (grey) are of equal average length (t2g are degenerate). The metal-metal bonds are shown, indicating degenerate interpenetrating 1D chains of ions. (b) Structural distortion (for example tetragonal along c-axis) lifts the degeneracy (making the (110)-type directions (green) special). (c) Dimerization along the (110)-type chains occurring in the low temperature insulating phases results in a redistribution of bond-lengths: each dimer converts two average distances to a pair of short (red) and long (blue) distances. Details of the three dimensional ordering of the dimers then depend on the specifics of the transitional metal spinel family.
