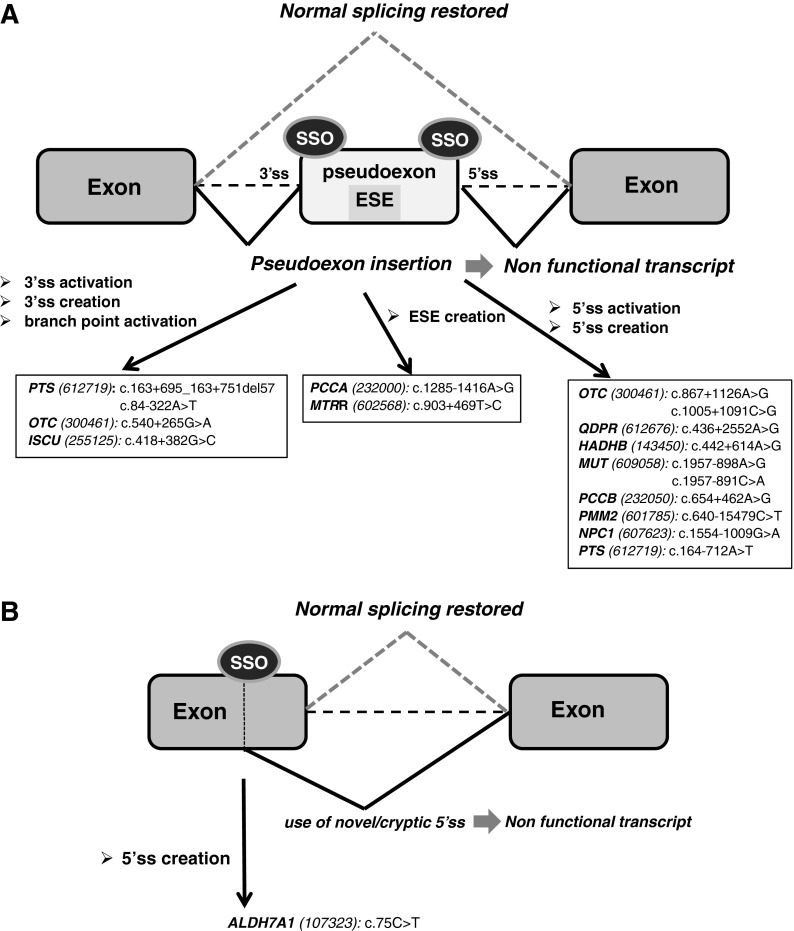
FIG. 1.
Use of splice-switching oligonucleotides (SSOs) to correct RNA splicing defects in inherited metabolic diseases (IMDs). The figure shows the schematics of the mechanisms of exonic and intronic mutations identified in patients causing splicing defects and their correction with antisense therapy. (A) SSO-induced pseudoexon skipping. (B) Use of SSOs to block mutation-created exonic splice sites or intronic cryptic splice sites. The arrows indicate the mutations and corresponding genes (MIM reference number in brackets) targeted by SSOs (as referenced in Desviat et al., 2006; Perez et al., 2010; Brasil et al., 2011; Sanaker et al., 2012; Perez et al., 2013). ESE, exonic splicing enhancer; 3′ss, 3′ splice site; 5′ss, 5′ splice site.