1.
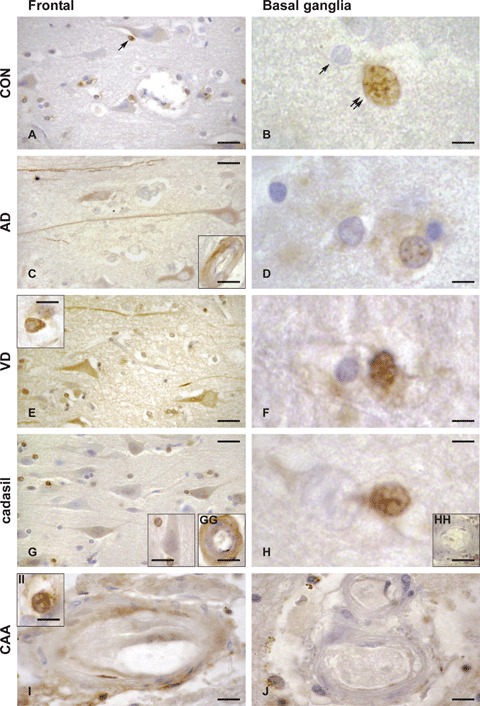
Expression of occludin in control (CON, A, B), Alzheimer's disease (AD, C, D), vascular dementia (VD, E, F), CADASIL (cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy, G, GG, H, HH) and CAA (congophilic amyloid angiopathy, I, II, J) brains, in the frontal medial gyrus Brodmann's area 9 (left panels, A, C, E, G, GG, I, II), and basal ganglia, nucleus caudatus (right panels, B, D, F, H, HH, J). Occludin-expressing cells are brownish, as a result of the immunohistochemical staining method with anti-occludin serum detected with avidin–biotin-peroxidase complex kit and DAB substrate. As compared to control brain, in AD and VD brains, occludin expression was increased in neurons and neuronal fibres in the frontal cortex (left panels, A, C, E, G), and in the glial cells of the basal ganglia (right panels, B, D, F, H). Inserts show occludin expression within the brain microvasculature (transversal sections) which is seen only in selected endothelial cells in AD (C) and CAA (I) and in the entire vessel wall in CADASIL (GG). The occludin expression pattern in neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes was similar to control for both CADASIL and CAA cases. Conversely, as compared to control, a more intense occludin expression was noted in the endothelium of CADASIL and CAA cases, mainly in the frontal cortex region. Occludin expression was noticed only in the pyramidal neurons (layer III in the figure) in AD and VD, but not in controls, CADASIL or CAA. Some selected oligodendroglial cells were occludin-positive in the frontal cortex region (arrow in A) in all cases analysed. Occludin-positive astrocytes were identified in VD (E, insert) and in CAA (II). Occludin expression was detected in the microvasculature of frontal cortex in AD (C, insert), CADASIL (GG) and sparsely in CAA (I), but not in control or VD. In the basal ganglia region, intranuclear staining was found almost only in astrocytes in control (B, double arrows, absence in oligodendrocytes denoted by single arrow), AD (D), VD (F) and CADASIL (H) brains. Occludin expression was undetectable in arteries of basal ganglia (nucleus caudatus) in all control and diseased brains (CADASIL, HH and CAA, J). Bars: 5 μm in B, D, F, H and II, 10 μm in E insert, G insert, GG, HH, I and J, 15 μm in A, C, E and G and 20 μm in C, insert.
