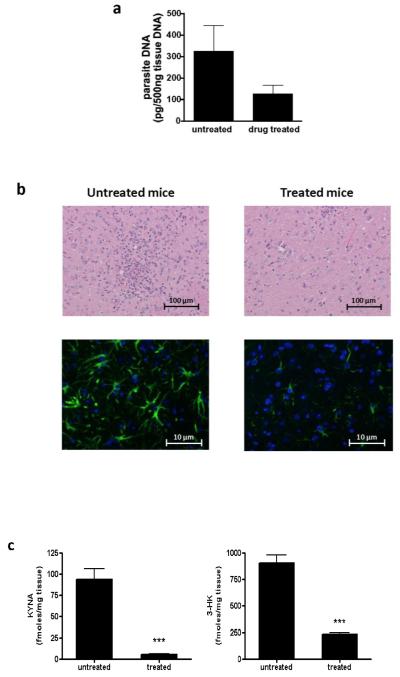
Fig. 5.
Treatment of T. gondii-infected mice with pyrimethamine/sulfadiazine reduces KP metabolite levels, inflammatory infiltrates and parasite burden. Infected mice were treated for 4 weeks with a combination of pyrimethamine/sulfadiazine, starting at 28 days post-infection (see Materials and methods for details). a) Real-time PCR specific for T. gondii DNA as measure of parasite burden in the brain; b) H & E staining (top panel) and GFAP staining (bottom panel) of brain sections of treated and untreated T. gondii-infected mice; c) KYNA and 3-HK brain levels in T. gondii-infected mice with (treated group) or without (untreated group) treatment. ***p<0.001 vs. untreated group (Student’s t-test).