Fig 1.
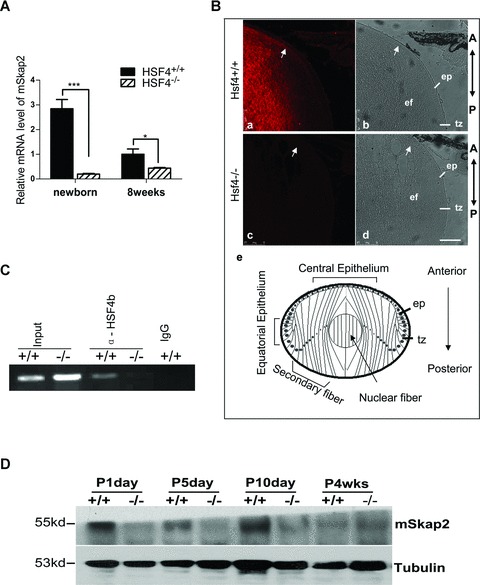
SKAP2 is down-regulated in HSF4−/− mouse lens. (A) mRNA was extracted from several lenses of newborn and adult (8 weeks) wild-type or HSF4−/− mice and assayed by quantitative RT-PCR. * denotes a significant difference compared to wild-type mice, P <0.05. (B) Fluorescent and light images of mid-sagittal sections from postnatal day 5 mice which were stained for endogenous mSKAP2. Parts a and b are from wild-type, parts c and d are from HSF4−/− mouse. The arrows point to the accumulating signal at the anterior tip of elongating secondary lens fibre cells, where they attach to the epithelium. Part e is a diagram of lens equatorial section. The bar represents 75 μm. ep: epithelium; tz: transition zone at equatorial epithelium; ef: elongating secondary fibre cells; A: anterior; P: posterior. (C) The nuclei of wild-type (+/+) and HSF4 knockout (−/−) mouse lens cells were extracted and immunoprecipitated with the goat anti-HSF4b antibody or with pre-immune IgG. Precipitated chromatin fragments were amplified using primers targeting the Skap2 promoter region around –500 bp. ‘Input’ indicates PCR amplification of the total DNA before precipitation. ‘IgG’ indicates pre-immune IgG. (D) SKAP2 protein was down-regulated in HSF4−/− mouse lens. SKAP2 was measured by the Western blotting from lens extracts (3 μg) of wild-type (+/+) and HSF4−/− (-/-) mice at postnatal days 1, 5 or 10; or at 4 weeks. Tubulin was re-blotted as the loading control.
