Fig 6.
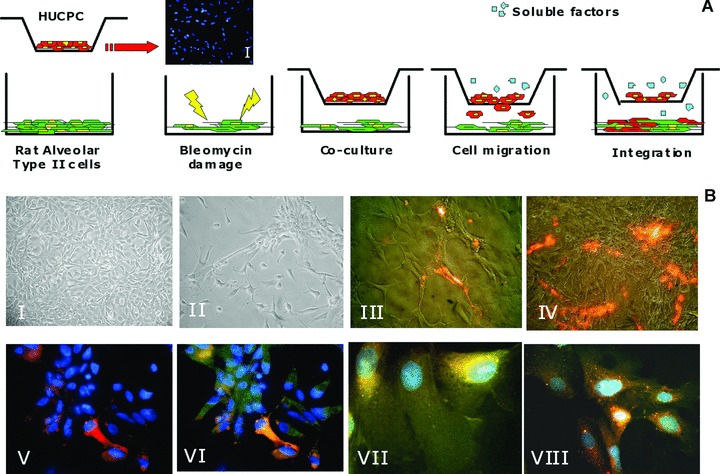
Foetal HUCPC migration assay. (A) Rat ATII cells, grown to 80% cell confluence in multiwell, were damaged exposing to bleomycin for 40 hrs. After 24 hrs foetal HUCPC, negative for the pro-surfactant protein C (I) and stained with the red fluorescent dye PKH26, were co-cultured in transwells in the presence of the damaged cell line. During 14 days of co-culture, foetal HUCPC migrate towards the rat ATII layer. Negative control was performed with a non-damaged rat ATII cell line under the same culture conditions. (B) The migration was continuously evaluated with inverted fluorescence microscope to observe the rat ATII cell line before the damage with bleomycin (I), after the damage (II), during the PKH26+ foetal HUCPC migration (III: red) and integration (IV: red). The migrated PKH26+ foetal HUCPC (V: red) co-expressed the epithelial alveolar marker pro-surfactant protein C (VI: green). Moreover, these cells maintain the expression of the perivascular markers CD146 (VII: green) and NG2 (VIII: green). All the cells (V–VIII) were stained with DAPI (blue).
