Fig 2.
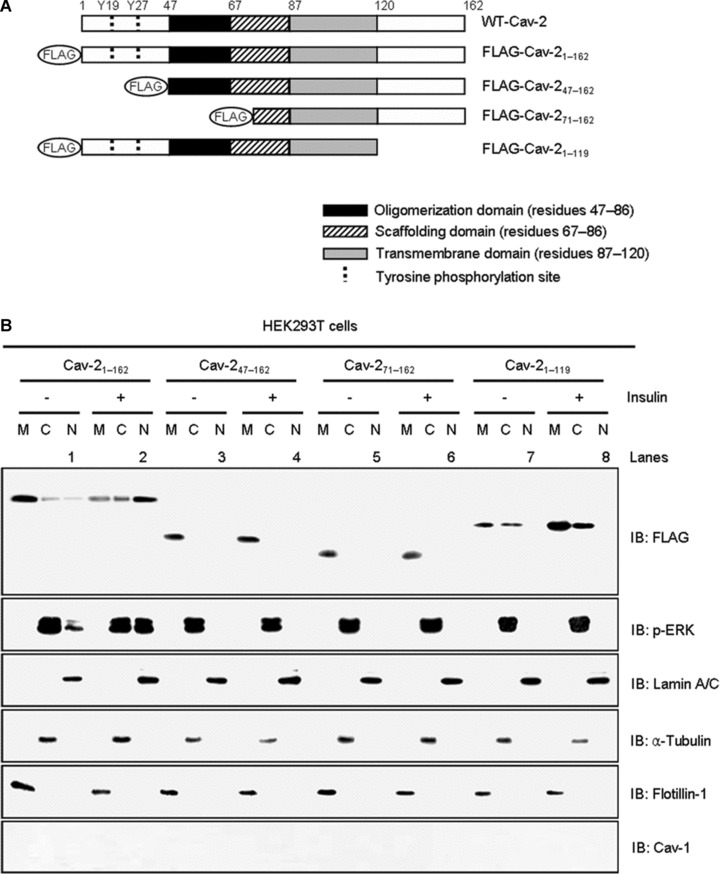
Effects of cav-2 domain deletion mutants on insulin-induced nuclear translocation of cav-2 and phospho-ERK. (A) A diagram of cav-2 deletion mutants. (B) HEK293T cells expressing FLAG-cav-21–162 or FLAG-cav-247–162, FLAG-cav-271–162, or FLAG-cav-21–119 mutants were treated with or without insulin (100 nM) for 10 min. and subjected to nuclear fractionation as described under ‘Materials and methods’. The fractions were analysed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted using antibodies against FLAG, phospho-ERK and cav-1, and detected with antibodies specific for lamin A/C, α-tubulin and flotillin-1 as markers for nuclear (N), cytoplasmic (C) and membrane (M) fractions, respectively. Shown is a representative experiment that was repeated three times.
